The interaction of trunk-load and trunk-position adaptations on knee anterior shear and hamstrings muscle forces during landing
- PMID: 20064042
- PMCID: PMC2808754
- DOI: 10.4085/1062-6050-45.1.5
The interaction of trunk-load and trunk-position adaptations on knee anterior shear and hamstrings muscle forces during landing
Abstract
Context: Because anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries can occur during deceleration maneuvers, biomechanics research has been focused on the lower extremity kinetic chain. Trunk mass and changes in trunk position affect lower extremity joint torques and work during gait and landing, but how the trunk affects knee joint and muscle forces is not well understood.
Objective: To evaluate the effects of added trunk load and adaptations to trunk position on knee anterior shear and knee muscle forces in landing.
Design: Crossover study.
Setting: Controlled laboratory environment.
Patients or other participants: Twenty-one participants (10 men: age = 20.3 +/- 1.15 years, height = 1.82 +/- 0.04 m, mass = 78.2 +/- 7.3 kg; 11 women: age = 20.0 +/- 1.10 years, height = 1.72 +/- 0.06 m, mass = 62.3 +/- 6.4 kg).
Intervention(s): Participants performed 2 sets of 8 double-leg landings under 2 conditions: no load and trunk load (10% body mass). Participants were categorized into one of 2 groups based on the kinematic trunk adaptation to the load: trunk flexor or trunk extensor.
Main outcome measure(s): We estimated peak and average knee anterior shear, quadriceps, hamstrings, and gastrocnemius forces with a biomechanical model.
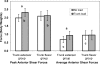
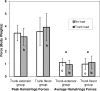
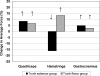
Results: We found condition-by-group interactions showing that adding a trunk load increased peak (17%) and average (35%) knee anterior shear forces in the trunk-extensor group but did not increase them in the trunk-flexor group (peak: F(1,19) = 10.56, P = .004; average: F(1,19) = 9.56, P = .006). We also found a main effect for condition for quadriceps and gastrocnemius forces. When trunk load was added, peak (6%; F(1,19) = 5.52, P = .030) and average (8%; F(1,19) = 8.83, P = .008) quadriceps forces increased and average (4%; F(1,19) = 4.94, P = .039) gastrocnemius forces increased, regardless of group. We found a condition-by-group interaction for peak (F(1,19) = 5.16, P = .035) and average (F(1,19) = 12.35, P = .002) hamstrings forces. When trunk load was added, average hamstrings forces decreased by 16% in the trunk-extensor group but increased by 13% in the trunk-flexor group.
Conclusions: Added trunk loads increased knee anterior shear and knee muscle forces, depending on trunk adaptation strategy. The trunk-extensor adaptation to the load resulted in a quadriceps-dominant strategy that increased knee anterior shear forces. Trunk-flexor adaptations may serve as a protective strategy against the added load. These findings should be interpreted with caution, as only the face validity of the biomechanical model was assessed.
Figures

References
-
- Krosshaug T., Nakamae A., Boden B. P., et al. Mechanisms of anterior cruciate ligament injury in basketball: video analysis of 39 cases. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):359–367. - PubMed
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. CDC Injury Research Agenda. http://www.cdc.gov/ncipc/pub-res/research_agenda/01_foreword.htm. Published June 2002. Accessed June 16, 2009.
-
- Beynnon B. D., Fleming B. C., Johnson R. J., Nichols C. E., Renström P. A., Pope M. H. Anterior cruciate ligament strain behavior during rehabilitation exercises in vivo. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(1):24–34. - PubMed
-
- Shelburne K. B., Torry M. R., Pandy M. G. Muscle, ligament, and joint-contact forces at the knee during walking. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(11):1948–1956. - PubMed
-
- DeMorat G., Weinhold P., Blackburn T., Chudik S., Garrett W. Aggressive quadriceps loading can induce noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injury. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(2):477–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

