Identification of a Rice stripe necrosis virus resistance locus and yield component QTLs using Oryza sativa x O. glaberrima introgression lines
- PMID: 20064202
- PMCID: PMC2824796
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-6
Identification of a Rice stripe necrosis virus resistance locus and yield component QTLs using Oryza sativa x O. glaberrima introgression lines
Abstract
Background: Developing new population types based on interspecific introgressions has been suggested by several authors to facilitate the discovery of novel allelic sources for traits of agronomic importance. Chromosome segment substitution lines from interspecific crosses represent a powerful and useful genetic resource for QTL detection and breeding programs.
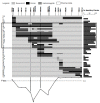
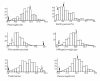
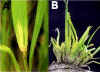
Results: We built a set of 64 chromosome segment substitution lines carrying contiguous chromosomal segments of African rice Oryza glaberrima MG12 (acc. IRGC103544) in the genetic background of Oryza sativa ssp. tropical japonica (cv. Caiapó). Well-distributed simple-sequence repeats markers were used to characterize the introgression events. Average size of the substituted chromosomal segments in the substitution lines was about 10 cM and covered the whole donor genome, except for small regions on chromosome 2 and 4. Proportions of recurrent and donor genome in the substitution lines were 87.59% and 7.64%, respectively. The remaining 4.78% corresponded to heterozygotes and missing data. Strong segregation distortion was found on chromosomes 3 and 6, indicating the presence of interspecific sterility genes. To illustrate the advantages and the power of quantitative trait loci (QTL) detection using substitution lines, a QTL detection was performed for scored traits. Transgressive segregation was observed for several traits measured in the population. Fourteen QTLs for plant height, tiller number per plant, panicle length, sterility percentage, 1000-grain weight and grain yield were located on chromosomes 1, 3, 4, 6 and 9. Furthermore, a highly significant QTL controlling resistance to the Rice stripe necrosis virus was located between SSR markers RM202-RM26406 (44.5-44.8 cM) on chromosome 11.
Conclusions: Development and phenotyping of CSSL libraries with entire genome coverage represents a useful strategy for QTL discovery. Mapping of the RSNV locus represents the first identification of a genetic factor underlying resistance to this virus. This population is a powerful breeding tool. It also helps in overcoming hybrid sterility barriers between species of rice.
Figures


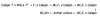
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

