Effort required to finish shotgun-generated genome sequences differs significantly among vertebrates
- PMID: 20064230
- PMCID: PMC2827409
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-21
Effort required to finish shotgun-generated genome sequences differs significantly among vertebrates
Abstract
Background: The approaches for shotgun-based sequencing of vertebrate genomes are now well-established, and have resulted in the generation of numerous draft whole-genome sequence assemblies. In contrast, the process of refining those assemblies to improve contiguity and increase accuracy (known as 'sequence finishing') remains tedious, labor-intensive, and expensive. As a result, the vast majority of vertebrate genome sequences generated to date remain at a draft stage.
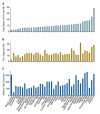
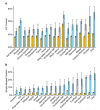
Results: To date, our genome sequencing efforts have focused on comparative studies of targeted genomic regions, requiring sequence finishing of large blocks of orthologous sequence (average size 0.5-2 Mb) from various subsets of 75 vertebrates. This experience has provided a unique opportunity to compare the relative effort required to finish shotgun-generated genome sequence assemblies from different species, which we report here. Importantly, we found that the sequence assemblies generated for the same orthologous regions from various vertebrates show substantial variation with respect to misassemblies and, in particular, the frequency and characteristics of sequence gaps. As a consequence, the work required to finish different species' sequences varied greatly. Application of the same standardized methods for finishing provided a novel opportunity to "assay" characteristics of genome sequences among many vertebrate species. It is important to note that many of the problems we have encountered during sequence finishing reflect unique architectural features of a particular vertebrate's genome, which in some cases may have important functional and/or evolutionary implications. Finally, based on our analyses, we have been able to improve our procedures to overcome some of these problems and to increase the overall efficiency of the sequence-finishing process, although significant challenges still remain.
Conclusion: Our findings have important implications for the eventual finishing of the draft whole-genome sequences that have now been generated for a large number of vertebrates.
Figures


References
-
- Wilson RK, Mardis ER. In: Genome Analysis: A laboratory manual: Analyzing DNA. Birren B, Green ED, Klapholz S, Myers RM, Roskams J, editor. Vol. 1. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1997. Shotgun sequencing; pp. 397–454.
-
- Blakesley RW, Hansen NF, Mullikin JC, Thomas PJ, McDowell JC, Maskeri B, Young AC, Benjamin B, Brooks SY, Coleman BI, Gupta J, Ho S-L, Karlins EM, Maduro QL, Stantripop S, Tsurgeon C, Vogt JL, Walker MA, Masiello CA, Guan X. NISC Comparative Sequencing Program. Bouffard GG, Green ED. An intermediate grade of finished genomic sequence suitable for comparative analysis. Genome Res. 2004;14:2235–2244. doi: 10.1101/gr.2648404. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

