Classic swine fever virus NS2 protein leads to the induction of cell cycle arrest at S-phase and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 20064240
- PMCID: PMC2819037
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-4
Classic swine fever virus NS2 protein leads to the induction of cell cycle arrest at S-phase and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
Background: Classical swine fever (CSF) caused by virulent strains of Classical swine fever virus (CSFV) is a haemorrhagic disease of pigs, characterized by disseminated intravascular coagulation, thrombocytopoenia and immunosuppression, and the swine endothelial vascular cell is one of the CSFV target cells. In this report, we investigated the previously unknown subcellular localization and function of CSFV NS2 protein by examining its effects on cell growth and cell cycle progression.
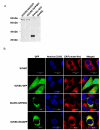
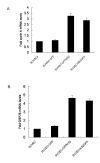
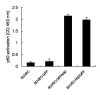
Results: Stable swine umbilical vein endothelial cell line (SUVEC) expressing CSFV NS2 were established and showed that the protein localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Cellular analysis revealed that replication of NS2-expressing cell lines was inhibited by 20-30% due to cell cycle arrest at S-phase. The NS2 protein also induced ER stress and activated the nuclear transcription factor kappa B (NF-kappaB). A significant increase in cyclin A transcriptional levels was observed in NS2-expressing cells but was accompanied by a concomitant increase in the proteasomal degradation of cyclin A protein. Therefore, the induction of cell cycle arrest at S-phase by CSFV NS2 protein is associated with increased turnover of cyclin A protein rather than the down-regulation of cyclin A transcription.
Conclusions: All the data suggest that CSFV NS2 protein modulate the cellular growth and cell cycle progression through inducing the S-phase arrest and provide a cellular environment that is advantageous for viral replication. These findings provide novel information on the function of the poorly characterized CSFV NS2 protein.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

