Design and validation of Segment--freely available software for cardiovascular image analysis
- PMID: 20064248
- PMCID: PMC2822815
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2342-10-1
Design and validation of Segment--freely available software for cardiovascular image analysis
Abstract
Background: Commercially available software for cardiovascular image analysis often has limited functionality and frequently lacks the careful validation that is required for clinical studies. We have already implemented a cardiovascular image analysis software package and released it as freeware for the research community. However, it was distributed as a stand-alone application and other researchers could not extend it by writing their own custom image analysis algorithms. We believe that the work required to make a clinically applicable prototype can be reduced by making the software extensible, so that researchers can develop their own modules or improvements. Such an initiative might then serve as a bridge between image analysis research and cardiovascular research. The aim of this article is therefore to present the design and validation of a cardiovascular image analysis software package (Segment) and to announce its release in a source code format.
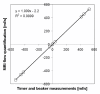
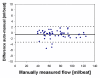
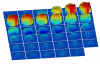
Results: Segment can be used for image analysis in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET). Some of its main features include loading of DICOM images from all major scanner vendors, simultaneous display of multiple image stacks and plane intersections, automated segmentation of the left ventricle, quantification of MRI flow, tools for manual and general object segmentation, quantitative regional wall motion analysis, myocardial viability analysis and image fusion tools. Here we present an overview of the validation results and validation procedures for the functionality of the software. We describe a technique to ensure continued accuracy and validity of the software by implementing and using a test script that tests the functionality of the software and validates the output. The software has been made freely available for research purposes in a source code format on the project home page http://segment.heiberg.se.
Conclusions: Segment is a well-validated comprehensive software package for cardiovascular image analysis. It is freely available for research purposes provided that relevant original research publications related to the software are cited.
Figures

References
-
- Engblom H, Hedström E, Heiberg E, Wagner GS, Pahlm O, Arheden H. Rapid initial reduction of hyperenhanced myocardium after reprefused first myocardial infarction suggest recovery of the peri-infarction zone: One year follow-up by MRI. Circulation Cardiovascular Imaging. 2009;48:47–55. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.108.802199. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heiberg E, Wigström L, Carlsson M, Bolger AF, Karlsson M. Time Resolved Three-dimensional Automated Segmentation of the Left Ventricle. IEEE Computers in Cardiology 2005; Lyon, France. 2005. pp. 599–602. full_text.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

