Assembly complexity of prokaryotic genomes using short reads
- PMID: 20064276
- PMCID: PMC2821320
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-21
Assembly complexity of prokaryotic genomes using short reads
Abstract
Background: De Bruijn graphs are a theoretical framework underlying several modern genome assembly programs, especially those that deal with very short reads. We describe an application of de Bruijn graphs to analyze the global repeat structure of prokaryotic genomes.
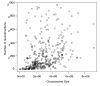
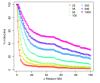
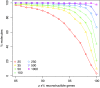
Results: We provide the first survey of the repeat structure of a large number of genomes. The analysis gives an upper-bound on the performance of genome assemblers for de novo reconstruction of genomes across a wide range of read lengths. Further, we demonstrate that the majority of genes in prokaryotic genomes can be reconstructed uniquely using very short reads even if the genomes themselves cannot. The non-reconstructible genes are overwhelmingly related to mobile elements (transposons, IS elements, and prophages).
Conclusions: Our results improve upon previous studies on the feasibility of assembly with short reads and provide a comprehensive benchmark against which to compare the performance of the short-read assemblers currently being developed.
Figures

References
-
- Solexa. http://www.solexa.com/
-
- Applied Biosystems. http://www.appliedbiosystems.com
-
- Harris TD, Buzby PR, Babcock H, Beer E, Bowers J, Braslavsky I, Causey M, Colonell J, Dimeo J, Efcavitch JW, Giladi E, Gill J, Healy J, Jarosz M, Lapen D, Moulton K, Quake SR, Steinmann K, Thayer E, Tyurina A, Ward R, Weiss H, Xie Z. Single-molecule DNA sequencing of a viral genome. Science. 2008;320(5872):106–109. doi: 10.1126/science.1150427. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

