Expression and characterization of soluble 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase from bacterial pathogens
- PMID: 20064433
- PMCID: PMC4020808
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2009.10.014
Expression and characterization of soluble 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase from bacterial pathogens
Abstract
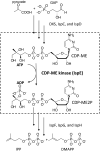
Many bacterial pathogens utilize the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway for biosynthesizing isoprenoid precursors, a pathway that is vital for bacterial survival and absent from human cells, providing a potential source of drug targets. However, the characterization of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol (CDP-ME) kinase (IspE) has been hindered due to a lack of enantiopure CDP-ME and difficulty in obtaining pure IspE. Here, enantiopure CDP-ME was chemically synthesized and recombinant IspE from bacterial pathogens were purified and characterized. Although gene disruption was not possible in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, IspE is essential in Mycobacterium smegmatis. The biochemical and kinetic characteristics of IspE provide the basis for development of a high throughput screen and structural characterization.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Synthesis of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2-phosphate and kinetic studies of Mycobacterium tuberculosis IspF.Chem Biol. 2010 Feb 26;17(2):117-22. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.01.013. Chem Biol. 2010. PMID: 20189102 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase (IspE) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.FASEB J. 2011 May;25(5):1577-84. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-175786. Epub 2011 Jan 31. FASEB J. 2011. PMID: 21282208
-
Characterization of Aquifex aeolicus 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-d-erythritol kinase - ligand recognition in a template for antimicrobial drug discovery.FEBS J. 2008 Jun;275(11):2779-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06418.x. Epub 2008 Apr 16. FEBS J. 2008. PMID: 18422643 Free PMC article.
-
Isoprenoid biosynthesis via 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate/2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (DOXP/MEP) pathway.Acta Biochim Pol. 2001;48(3):663-72. Acta Biochim Pol. 2001. PMID: 11833775 Review.
-
The methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis as a target for the development of new drugs against tuberculosis.Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(9):1325-38. doi: 10.2174/092986711795029582. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21366531 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis of Fusobacterium necrophorum Provides Insights into Conserved Virulence Genes.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0029722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00297-22. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36219094 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of chirally pure 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate : A substrate for IspC assay to determine M. tb inhibitor.Chem Sci J. 2013 Dec 30;4(2):22305. Chem Sci J. 2013. PMID: 24860687 Free PMC article.
-
Formal Synthesis of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl D-erythritol From D-(+)-Arabitol.Tetrahedron. 2012 Oct 28;68(43):8937-8941. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2012.08.020. Tetrahedron. 2012. PMID: 23049145 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating Novel IspE Inhibitors of the MEP Pathway in Mycobacterium.Microorganisms. 2023 Dec 21;12(1):18. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010018. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38276186 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged-acting, multi-targeting gallium nanoparticles potently inhibit growth of both HIV and mycobacteria in co-infected human macrophages.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 6;5:8824. doi: 10.1038/srep08824. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25744727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreassi JL, Leyh TS. Molecular functions of conserved aspects of the GHMP kinase family. Biochemistry. 2004;43:14594–14601. - PubMed
-
- Bernal C, Mendez E, Terencio J, Boronat A, Imperial S. A spectrophotometric assay for the determination of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase activity. Anal Biochem. 2005;340:245–251. - PubMed
-
- Cassera MB, Gozzo FC, D'Alexandri FL, Merino EF, del Portillo HA, Peres VJ, Almeida IC, Eberlin MN, Wunderlich G, Wiesner J, Jomaa H, Kimura EA, Katzin AM. The methylerythritol phosphate pathway is functionally active in all intraerythrocytic stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:51749–51759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

