Expression and characterization of soluble 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase from bacterial pathogens
- PMID: 20064433
- PMCID: PMC4020808
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2009.10.014
Expression and characterization of soluble 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase from bacterial pathogens
Abstract
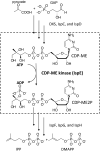
Many bacterial pathogens utilize the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway for biosynthesizing isoprenoid precursors, a pathway that is vital for bacterial survival and absent from human cells, providing a potential source of drug targets. However, the characterization of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol (CDP-ME) kinase (IspE) has been hindered due to a lack of enantiopure CDP-ME and difficulty in obtaining pure IspE. Here, enantiopure CDP-ME was chemically synthesized and recombinant IspE from bacterial pathogens were purified and characterized. Although gene disruption was not possible in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, IspE is essential in Mycobacterium smegmatis. The biochemical and kinetic characteristics of IspE provide the basis for development of a high throughput screen and structural characterization.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Andreassi JL, Leyh TS. Molecular functions of conserved aspects of the GHMP kinase family. Biochemistry. 2004;43:14594–14601. - PubMed
-
- Bernal C, Mendez E, Terencio J, Boronat A, Imperial S. A spectrophotometric assay for the determination of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase activity. Anal Biochem. 2005;340:245–251. - PubMed
-
- Cassera MB, Gozzo FC, D'Alexandri FL, Merino EF, del Portillo HA, Peres VJ, Almeida IC, Eberlin MN, Wunderlich G, Wiesner J, Jomaa H, Kimura EA, Katzin AM. The methylerythritol phosphate pathway is functionally active in all intraerythrocytic stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:51749–51759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

