Controlling hematopoiesis through sumoylation-dependent regulation of a GATA factor
- PMID: 20064464
- PMCID: PMC2807411
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.005
Controlling hematopoiesis through sumoylation-dependent regulation of a GATA factor
Abstract
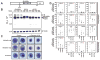
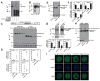
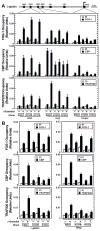
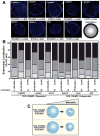
GATA factors establish transcriptional networks that control fundamental developmental processes. Whereas the regulator of hematopoiesis GATA-1 is subject to multiple posttranslational modifications, how these modifications influence GATA-1 function at endogenous loci is unknown. We demonstrate that sumoylation of GATA-1 K137 promotes transcriptional activation only at target genes requiring the coregulator Friend of GATA-1 (FOG-1). A mutation of GATA-1 V205G that disrupts FOG-1 binding and K137 mutations yielded similar phenotypes, although sumoylation was FOG-1 independent, and FOG-1 binding did not require sumoylation. Both mutations dysregulated GATA-1 chromatin occupancy at select sites, FOG-1-dependent gene expression, and were rescued by tethering SUMO-1. While FOG-1- and SUMO-1-dependent genes migrated away from the nuclear periphery upon erythroid maturation, FOG-1- and SUMO-1-independent genes persisted at the periphery. These results illustrate a mechanism that controls trans-acting factor function in a locus-specific manner, and differentially regulated members of the target gene ensemble reside in distinct subnuclear compartments.
2009 Elsevier Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Relocalizing genetic loci into specific subnuclear neighborhoods.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 27;286(21):18834-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.221481. Epub 2011 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21398517 Free PMC article.
-
Cofactor-mediated restriction of GATA-1 chromatin occupancy coordinates lineage-specific gene expression.Mol Cell. 2012 Aug 24;47(4):608-21. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.051. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22771118 Free PMC article.
-
Differential coregulator requirements for function of the hematopoietic transcription factor GATA-1 at endogenous loci.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Apr;38(7):2190-200. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1159. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20047963 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating Transcriptional Coregulator Ensembles to Establish Genetic Networks: A GATA Factor Perspective.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016;118:205-44. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27137658 Review.
-
The Regulation of Chromatin by Dynamic SUMO Modifications.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1475:23-38. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6358-4_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27631795 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin loop formation in the β-globin locus and its role in globin gene transcription.Mol Cells. 2012 Jul;34(1):1-5. doi: 10.1007/s10059-012-0048-8. Epub 2012 May 18. Mol Cells. 2012. PMID: 22610406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relocalizing genetic loci into specific subnuclear neighborhoods.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 27;286(21):18834-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.221481. Epub 2011 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21398517 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation regulates the chromatin occupancy and anti-proliferative gene programs of glucocorticoid receptor.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Feb;42(3):1575-92. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1033. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24194604 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a cell-type-specific genetic network by the mediator complex component Med1.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 May;33(10):1938-55. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00141-13. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23459945 Free PMC article.
-
A deficiency in SUMOylation activity disrupts multiple pathways leading to neural tube and heart defects in Xenopus embryos.BMC Genomics. 2019 May 17;20(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5773-3. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31101013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anguita E, Sharpe JA, Sloane-Stanley JA, Tufarelli C, Higgs DR, Wood WG. Deletion of the mouse alpha-globin regulatory element (HS-26) has an unexpectedly mild phenotype. Blood. 2002;100:3450–3456. - PubMed
-
- Bresnick EH, Johnson KD, Kim SI, Im H. Establishment and regulation of chromatin domains: mechanistic insights from studies of hemoglobin synthesis. Prog Nucl Acids Res Mol Biol. 2006;81:435–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

