Sequence-specific intramembrane proteolysis: identification of a recognition motif in rhomboid substrates
- PMID: 20064469
- PMCID: PMC2941825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.006
Sequence-specific intramembrane proteolysis: identification of a recognition motif in rhomboid substrates
Abstract
Members of the widespread rhomboid family of intramembrane proteases cleave transmembrane domain (TMD) proteins to regulate processes as diverse as EGF receptor signaling, mitochondrial dynamics, and invasion by apicomplexan parasites. However, lack of information about their substrates means that the biological role of most rhomboids remains obscure. Knowledge of how rhomboids recognize their substrates would illuminate their mechanism and might also allow substrate prediction. Previous work has suggested that rhomboid substrates are specified by helical instability in their TMD. Here we demonstrate that rhomboids instead primarily recognize a specific sequence surrounding the cleavage site. This recognition motif is necessary for substrate cleavage, it determines the cleavage site, and it is more strictly required than TM helix-destabilizing residues. Our work demonstrates that intramembrane proteases can be sequence specific and that genome-wide substrate prediction based on their recognition motifs is feasible.
2009 Elsevier Inc.
Figures
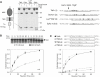
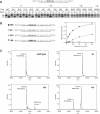


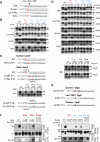

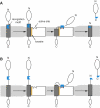
Comment in
-
Rhomboid proteases: familiar features in unfamiliar phases.Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 25;36(6):922-3. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.12.005. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 20064458
Similar articles
-
Substrate specificity of rhomboid intramembrane proteases is governed by helix-breaking residues in the substrate transmembrane domain.Mol Cell. 2003 Jun;11(6):1425-34. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00181-3. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12820957
-
Conservation of intramembrane proteolytic activity and substrate specificity in prokaryotic and eukaryotic rhomboids.Curr Biol. 2002 Sep 3;12(17):1507-12. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01092-8. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12225666
-
Reconstitution of intramembrane proteolysis in vitro reveals that pure rhomboid is sufficient for catalysis and specificity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 8;102(6):1883-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408306102. Epub 2005 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15684070 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of rhomboid family proteins in mammalian biology and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1828(12):2840-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.03.025. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23562403 Review.
-
Structural and mechanistic principles of intramembrane proteolysis--lessons from rhomboids.FEBS J. 2013 Apr;280(7):1579-603. doi: 10.1111/febs.12199. Epub 2013 Mar 20. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23432912 Review.
Cited by
-
Pink1 kinase and its membrane potential (Deltaψ)-dependent cleavage product both localize to outer mitochondrial membrane by unique targeting mode.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 29;287(27):22969-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.365700. Epub 2012 Apr 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22547060 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane proteases in the bacterial protein secretion and quality control pathway.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Jun;76(2):311-30. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05019-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22688815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhomboid intramembrane protease YqgP licenses bacterial membrane protein quality control as adaptor of FtsH AAA protease.EMBO J. 2020 May 18;39(10):e102935. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019102935. Epub 2020 Jan 13. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 31930742 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple downy mildew effectors target the stress-related NAC transcription factor LsNAC069 in lettuce.Plant J. 2019 Sep;99(6):1098-1115. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14383. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Plant J. 2019. PMID: 31077456 Free PMC article.
-
Signal peptide peptidase functions in ERAD to cleave the unfolded protein response regulator XBP1u.EMBO J. 2014 Nov 3;33(21):2492-506. doi: 10.15252/embj.201488208. Epub 2014 Sep 19. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 25239945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama Y., Maegawa S. Sequence features of substrates required for cleavage by GlpG, an Escherichia coli rhomboid protease. Mol. Microbiol. 2007;64:1028–1037. - PubMed
-
- Chao J.R., Parganas E., Boyd K., Hong C.Y., Opferman J.T., Ihle J.N. Hax1-mediated processing of HtrA2 by Parl allows survival of lymphocytes and neurons. Nature. 2008;452:98–102. - PubMed
-
- Engelman D.M., Steitz T.A., Goldman A. Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 1986;15:321–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

