Refined QTLs of osteoporosis-related traits by linkage analysis with genome-wide SNPs: Framingham SHARe
- PMID: 20064633
- PMCID: PMC2842472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2010.01.001
Refined QTLs of osteoporosis-related traits by linkage analysis with genome-wide SNPs: Framingham SHARe
Abstract
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) using high-density array of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) offer an unbiased strategy to identify new candidate genes for osteoporosis. We used a subset of autosomal SNPs from the Affymetrix 500K+50K SNP GeneChip marker set to examine genetic linkage with multiple highly heritable osteoporosis-related traits, including BMD of the hip and spine, heel ultrasound (attenuation and speed of sound), and geometric indices of the hip, in two generations from the Framingham Osteoporosis Study. Variance component linkage analysis was performed using normalized residuals (adjusted for age, height, BMI, and estrogen status in women). Multipoint linkage analyses produced LOD scores > or =3.0 for BMD on chromosomes (chr.) 9 and 11 and for ultrasound speed of sound on chr. 5. Hip geometric traits were linked with higher LOD scores, such as with shaft width on chr. 4 (LOD=3.9) and chr. 16 (LOD=3.8) and with shaft section modulus on chr. 22 (LOD=4.0). LOD score > or =5.0 was obtained for femoral neck width on chr. 7. In conclusion, with an SNP-based linkage approach, we identified several novel potential QTLs and confirmed previously identified chromosomal regions linked to bone mass and geometry. Subsequent focus on the spectrum of genetic polymorphisms in these refined regions may contribute to finding variants predisposing to osteoporosis.
Keywords: BMD; SNP array; bone geometry; osteoporosis; quantitative trait loci.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
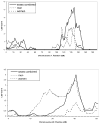
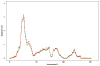
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide association with bone mass and geometry in the Framingham Heart Study.BMC Med Genet. 2007 Sep 19;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S14. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-8-S1-S14. BMC Med Genet. 2007. PMID: 17903296 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide pleiotropy of osteoporosis-related phenotypes: the Framingham Study.J Bone Miner Res. 2010 Jul;25(7):1555-63. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.38. J Bone Miner Res. 2010. PMID: 20200953 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal hip geometry is linked to several chromosomal regions: genome-wide linkage results from the Framingham Osteoporosis Study.Bone. 2007 Mar;40(3):743-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.09.020. Epub 2006 Oct 31. Bone. 2007. PMID: 17079199 Free PMC article.
-
Collaborative meta-analysis: associations of 150 candidate genes with osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture.Ann Intern Med. 2009 Oct 20;151(8):528-37. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-8-200910200-00006. Ann Intern Med. 2009. PMID: 19841454 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of osteoporosis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Sep 19;452(2):287-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.07.141. Epub 2014 Aug 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25139232 Review.
Cited by
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism-single nucleotide polymorphism interactions among inflammation genes in the genetic architecture of blood pressure in the Framingham Heart Study.Am J Hypertens. 2015 Feb;28(2):248-55. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpu132. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Am J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25063733 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide approaches for identifying genetic risk factors for osteoporosis.Genome Med. 2013 May 29;5(5):44. doi: 10.1186/gm448. eCollection 2013. Genome Med. 2013. PMID: 23731620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide linkage scan for quantitative trait loci underlying normal variation in heel bone ultrasound measures.J Nutr Health Aging. 2012 Jan;16(1):8-13. doi: 10.1007/s12603-011-0080-y. J Nutr Health Aging. 2012. PMID: 22237995 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of serum osteocalcin and bone mineral in multigenerational Afro-Caribbean families.Osteoporos Int. 2012 May;23(5):1521-31. doi: 10.1007/s00198-011-1763-2. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Osteoporos Int. 2012. PMID: 21935688 Free PMC article.
-
Digital Clock Drawing as an Alzheimer's Disease Susceptibility Biomarker: Associations with Genetic Risk Score and APOE in Older Adults.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2024;11(1):79-87. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2023.48. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38230720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR. Merlin--rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet. 2002;30:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Arden NK, Baker J, Hogg C, Baan K, Spector TD. The heritability of bone mineral density, ultrasound of the calcaneus and hip axis length: a study of postmenopausal twins. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 1996;11:530–4. - PubMed
-
- Beck TJ, Ruff CB, Scott WW, Jr, Plato CC, Tobin JD, Quan CA. Sex differences in geometry of the femoral neck with aging: a structural analysis of bone mineral data. Calcif Tissue Int. 1992;50:24–9. - PubMed
-
- Benyamin B, Visscher PM, McRae AF. Family-based genome-wide association studies. Pharmacogenomics. 2009;10:181–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

