Microwaves from Mobile Phones Inhibit 53BP1 Focus Formation in Human Stem Cells More Strongly Than in Differentiated Cells: Possible Mechanistic Link to Cancer Risk
- PMID: 20064781
- PMCID: PMC2854769
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.0900781
Microwaves from Mobile Phones Inhibit 53BP1 Focus Formation in Human Stem Cells More Strongly Than in Differentiated Cells: Possible Mechanistic Link to Cancer Risk
Abstract
Background: It is widely accepted that DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and their misrepair in stem cells are critical events in the multistage origination of various leukemias and tumors, including gliomas.
Objectives: We studied whether microwaves from mobile telephones of the Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) and the Universal Global Telecommunications System (UMTS) induce DSBs or affect DSB repair in stem cells.
Methods: We analyzed tumor suppressor TP53 binding protein 1 (53BP1) foci that are typically formed at the sites of DSB location (referred to as DNA repair foci) by laser confocal microscopy.
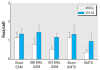
Results: Microwaves from mobile phones inhibited formation of 53BP1 foci in human primary fibroblasts and mesenchymal stem cells. These data parallel our previous findings for human lymphocytes. Importantly, the same GSM carrier frequency (915 MHz) and UMTS frequency band (1947.4 MHz) were effective for all cell types. Exposure at 905 MHz did not inhibit 53BP1 foci in differentiated cells, either fibroblasts or lymphocytes, whereas some effects were seen in stem cells at 905 MHz. Contrary to fibroblasts, stem cells did not adapt to chronic exposure during 2 weeks.
Conclusions: The strongest microwave effects were always observed in stem cells. This result may suggest both significant misbalance in DSB repair and severe stress response. Our findings that stem cells are most sensitive to microwave exposure and react to more frequencies than do differentiated cells may be important for cancer risk assessment and indicate that stem cells are the most relevant cellular model for validating safe mobile communication signals.
Keywords: 53BP1 foci; DNA double-strand breaks; microwaves; mobile phones; stem cells.
Figures
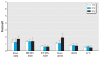
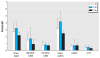

Similar articles
-
Microwaves from UMTS/GSM mobile phones induce long-lasting inhibition of 53BP1/gamma-H2AX DNA repair foci in human lymphocytes.Bioelectromagnetics. 2009 Feb;30(2):129-41. doi: 10.1002/bem.20445. Bioelectromagnetics. 2009. PMID: 18839414
-
Microwaves from GSM mobile telephones affect 53BP1 and gamma-H2AX foci in human lymphocytes from hypersensitive and healthy persons.Environ Health Perspect. 2005 Sep;113(9):1172-7. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7561. Environ Health Perspect. 2005. PMID: 16140623 Free PMC article.
-
915 MHz microwaves and 50 Hz magnetic field affect chromatin conformation and 53BP1 foci in human lymphocytes from hypersensitive and healthy persons.Bioelectromagnetics. 2005 Apr;26(3):173-84. doi: 10.1002/bem.20103. Bioelectromagnetics. 2005. PMID: 15768430 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Mobile Phone-Induced Electromagnetic Field on Brain Hemodynamics and Human Stem Cell Functioning: Possible Mechanistic Link to Cancer Risk and Early Diagnostic Value of Electronphotonic Imaging.J Stem Cells. 2015;10(4):287-94. J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 27144830 Review.
-
Roles for 53BP1 in the repair of radiation-induced DNA double strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Sep;93:102915. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102915. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33087281 Review.
Cited by
-
New Zealand adolescents' cellphone and cordless phone user-habits: are they at increased risk of brain tumours already? A cross-sectional study.Environ Health. 2013 Jan 10;12:5. doi: 10.1186/1476-069X-12-5. Environ Health. 2013. PMID: 23302218 Free PMC article.
-
Cell type-dependent induction of DNA damage by 1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic fields does not result in significant cellular dysfunctions.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054906. Epub 2013 Jan 23. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23355902 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Microwaves from mobile phone induce reactive oxygen species but not DNA damage, preleukemic fusion genes and apoptosis in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 7;9(1):16182. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52389-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31700008 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Density Geopolymer Composites for the Construction Industry.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jan 13;14(2):304. doi: 10.3390/polym14020304. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35054711 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of RF-EMF Exposure from GSM Mobile Phones on Proliferation Rate of Human Adipose-derived Stem Cells: An In-vitro Study.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2016 Dec 1;6(4):243-252. eCollection 2016 Dec. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2016. PMID: 28144594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adey WR. Tissue interactions with nonionizing electromagnetic fields. Physiol Rev. 1981;61(2):435–514. - PubMed
-
- Altaner C. Glioblastoma and stem cells. Neoplasma. 2008;55(5):369–374. - PubMed
-
- Banath JP, Banuelos CA, Klokov D, MacPhail SM, Lansdorp PM, Olive PL. Explanation for excessive DNA single-strand breaks and endogenous repair foci in pluripotent mouse embryonic stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(8):1505–1520. - PubMed
-
- Banath JP, Macphail SH, Olive PL. Radiation sensitivity, H2AX phosphorylation, and kinetics of repair of DNA strand breaks in irradiated cervical cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2004;64(19):7144–7149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

