MedEx: a medication information extraction system for clinical narratives
- PMID: 20064797
- PMCID: PMC2995636
- DOI: 10.1197/jamia.M3378
MedEx: a medication information extraction system for clinical narratives
Abstract
Medication information is one of the most important types of clinical data in electronic medical records. It is critical for healthcare safety and quality, as well as for clinical research that uses electronic medical record data. However, medication data are often recorded in clinical notes as free-text. As such, they are not accessible to other computerized applications that rely on coded data. We describe a new natural language processing system (MedEx), which extracts medication information from clinical notes. MedEx was initially developed using discharge summaries. An evaluation using a data set of 50 discharge summaries showed it performed well on identifying not only drug names (F-measure 93.2%), but also signature information, such as strength, route, and frequency, with F-measures of 94.5%, 93.9%, and 96.0% respectively. We then applied MedEx unchanged to outpatient clinic visit notes. It performed similarly with F-measures over 90% on a set of 25 clinic visit notes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
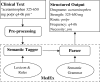

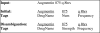

References
-
- Johnson KB, Kiepek W. Outpatient e-prescribing at an academic medical center [case study]. In: Mansur JM. (ed.). A guide to the Joint Commission's Medication Management Standards. Joint Commission Resources (JCR), 2009:120–7
-
- JCAHO 2005 National patient safety goals. http://www.jointcommission.org/patientsafety/nationalpatientsafetygoals/... 2005. (accessed 15 Nov 2009).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

