Decimal place slope, a fast and precise method for quantifying 13C incorporation levels for detecting the metabolic activity of microbial species
- PMID: 20064840
- PMCID: PMC2877982
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M900407-MCP200
Decimal place slope, a fast and precise method for quantifying 13C incorporation levels for detecting the metabolic activity of microbial species
Abstract
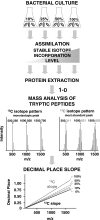
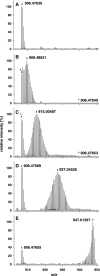
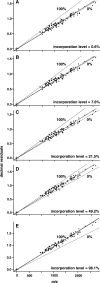
The metabolic incorporation of stable isotopes such as (13)C or (15)N into proteins has become a powerful tool for qualitative and quantitative proteome studies. We recently introduced a method that monitors heavy isotope incorporation into proteins and presented data revealing the metabolic activity of various species in a microbial consortium using this technique. To further develop our method using an liquid chromatography (LC)-mass spectrometry (MS)-based approach, we present here a novel approach for calculating the incorporation level of (13)C into peptides by using the information given in the decimal places of peptide masses obtained by modern high-resolution MS. In the present study, the applicability of this approach is demonstrated using Pseudomonas putida ML2 proteins uniformly labeled via the consumption of [(13)C(6)]benzene present in the medium at concentrations of 0, 10, 25, 50, and 100 atom %. The incorporation of (13)C was calculated on the basis of several labeled peptides derived from one band on an SDS-PAGE gel. The accuracy of the calculated incorporation level depended upon the number of peptide masses included in the analysis, and it was observed that at least 100 peptide masses were required to reduce the deviation below 4 atom %. This accuracy was comparable with calculations of incorporation based on the isotope envelope. Furthermore, this method can be extended to the calculation of the labeling efficiency for a wide range of biomolecules, including RNA and DNA. The technique will therefore allow a highly accurate determination of the carbon flux in microbial consortia with a direct approach based solely on LC-MS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insights from quantitative metaproteomics and protein-stable isotope probing into microbial ecology.ISME J. 2013 Oct;7(10):1877-85. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.78. Epub 2013 May 16. ISME J. 2013. PMID: 23677009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incorporation of carbon and nitrogen atoms into proteins measured by protein-based stable isotope probing (Protein-SIP).Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2008 Sep;22(18):2889-97. doi: 10.1002/rcm.3684. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2008. PMID: 18727149
-
Calculation of partial isotope incorporation into peptides measured by mass spectrometry.BMC Res Notes. 2010 Jun 24;3:178. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-3-178. BMC Res Notes. 2010. PMID: 20576105 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the limits of robust detection of incorporation of 13C by mass spectrometry in protein-based stable isotope probing (protein-SIP).Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011 Oct;401(6):1975-82. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5289-4. Epub 2011 Aug 7. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21822970
-
Isotopes in geobiochemistry: tracing metabolic pathways in microorganisms of environmental relevance with stable isotopes.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2016 Oct;41:19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2016.03.018. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27085100 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative tracking of isotope flows in proteomes of microbial communities.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Apr;10(4):M110.006049. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M110.006049. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21285414 Free PMC article.
-
Poisson Model To Generate Isotope Distribution for Biomolecules.J Proteome Res. 2018 Jan 5;17(1):751-758. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00807. Epub 2017 Dec 19. J Proteome Res. 2018. PMID: 29202576 Free PMC article.
-
A Mechanism to Transform Complex Salicinoids with Caffeoylquinic Acids in Lepidopteran Specialist Herbivores (Notodontidae).J Chem Ecol. 2024 Feb;50(1-2):71-83. doi: 10.1007/s10886-023-01464-9. Epub 2023 Nov 30. J Chem Ecol. 2024. PMID: 38030933 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-based stable isotope probing.Nat Protoc. 2010 Dec;5(12):1957-66. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2010.166. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Nat Protoc. 2010. PMID: 21127489
-
Insights from quantitative metaproteomics and protein-stable isotope probing into microbial ecology.ISME J. 2013 Oct;7(10):1877-85. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.78. Epub 2013 May 16. ISME J. 2013. PMID: 23677009 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bantscheff M., Schirle M., Sweetman G., Rick J., Kuster B. (2007) Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: a critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 389, 1017–1031 - PubMed
-
- Friedrich M. W. (2006) Stable-isotope probing of DNA: insights into the function of uncultivated microorganisms from isotopically labeled metagenomes. Curr. Opin. Biotech 17, 59–66 - PubMed
-
- Jehmlich N., Schmidt F., von Bergen M., Richnow H. H., Vogt C. (2008) Protein-based stable isotope probing (Protein-SIP) reveals active species within anoxic mixed cultures. ISME J 2, 1122–1133 - PubMed
-
- Ong S. E., Blagoev B., Kratchmarova I., Kristensen D. B., Steen H., Pandey A., Mann M. (2002) Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and accurate approach to expression proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 1, 376–386 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

