Targeted PPAR{gamma} deficiency in alveolar macrophages disrupts surfactant catabolism
- PMID: 20064973
- PMCID: PMC3035495
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M001651
Targeted PPAR{gamma} deficiency in alveolar macrophages disrupts surfactant catabolism
Abstract
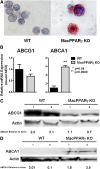
Surfactant accumulates in alveolar macrophages of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) knockout (KO) mice and pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) patients with a functional loss of GM-CSF resulting from neutralizing anti-GM-CSF antibody. Alveolar macrophages from PAP patients and GM-CSF KO mice are de-ficient in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma) and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) lipid transporter ABCG1. Previous studies have demonstrated that GM-CSF induces PPARgamma. We therefore hypothesized that PPARgamma promotes surfactant catabolism through regulation of ABCG1. To address this hypothesis, macrophage-specific PPARgamma (MacPPARgamma) knockout mice were utilized. MacPPARgamma KO mice develop foamy, lipid-engorged Oil Red O positive alveolar macrophages. Lipid analyses revealed significant increases in the cholesterol and phospholipid contents of MacPPARgamma KO alveolar macrophages and extracellular bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)-derived fluids. MacPPARgamma KO alveolar macrophages showed decreased expression of ABCG1 and a deficiency in ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux to HDL. Lipid metabolism may also be regulated by liver X receptor (LXR)-ABCA1 pathways. Interestingly, ABCA1 and LXRbeta expression were elevated, indicating that this pathway is not sufficient to prevent surfactant accumulation in alveolar macrophages. These results suggest that PPARgamma mediates a critical role in surfactant homeostasis through the regulation of ABCG1.
Figures



References
-
- Thomassen M. J., Yi T., Raychaudhuri B., Malur A., Kavuru M. S. 2000. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis is a disease of decreased availability of GM-CSF rather than an intrinsic cellular defect. Clin. Immunol. 95: 85–92. - PubMed
-
- Sorensen G. L., Husby S., Holmskov U. 2007. Surfactant protein A and surfactant protein D variation in pulmonary disease. Immunobiology. 212: 381–416. - PubMed
-
- Trapnell B. C., Whitsett J. A. 2002. GM-CSF regulates pulmonary surfactant homeostasis and alveolar macrophage-mediated innate host defense. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64: 775–802. - PubMed
-
- Veldhuizen R., Nag K., Orgeig S., Possmayer F. 1998. The role of lipids in pulmonary surfactant. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1408: 90–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

