Identification of a c-di-GMP-regulated polysaccharide locus governing stress resistance and biofilm and rugose colony formation in Vibrio vulnificus
- PMID: 20065022
- PMCID: PMC2825937
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01188-09
Identification of a c-di-GMP-regulated polysaccharide locus governing stress resistance and biofilm and rugose colony formation in Vibrio vulnificus
Abstract
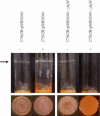
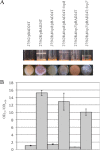
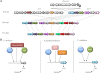
As an etiological agent of bacterial sepsis and wound infections, Vibrio vulnificus is unique among the Vibrionaceae. Its continued environmental persistence and transmission are bolstered by its ability to colonize shellfish, form biofilms on various marine biotic surfaces, and generate a morphologically and physiologically distinct rugose (R) variant that yields profuse biofilms. Here, we identify a c-di-GMP-regulated locus (brp, for biofilm and rugose polysaccharide) and two transcription factors (BrpR and BrpT) that regulate these physiological responses. Disruption of glycosyltransferases within the locus or either regulator abated the inducing effect of c-di-GMP on biofilm formation, rugosity, and stress resistance. The same lesions, or depletion of intracellular c-di-GMP levels, abrogated these phenotypes in the R variant. The parental and brp mutant strains formed only scant monolayers on glass surfaces and oyster shells, and although the R variant formed expansive biofilms, these were of limited depth. Dramatic vertical expansion of the biofilm structure was observed in the parental strain and R variant, but not the brp mutants, when intracellular c-di-GMP levels were elevated. Hence, the brp-encoded polysaccharide is important for surface colonization and stress resistance in V. vulnificus, and its expression may control how the bacteria switch from a planktonic lifestyle to colonizing shellfish to invading human tissue.
Figures

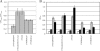

Similar articles
-
Complex Control of a Genomic Island Governing Biofilm and Rugose Colony Development in Vibrio vulnificus.J Bacteriol. 2018 Jul 25;200(16):e00190-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00190-18. Print 2018 Aug 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29760209 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping and unique contributions of two conserved polysaccharide loci in governing distinct survival phenotypes in Vibrio vulnificus.Environ Microbiol. 2011 Nov;13(11):2888-990. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02564.x. Epub 2011 Sep 5. Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21895917
-
Environmental Calcium Initiates a Feed-Forward Signaling Circuit That Regulates Biofilm Formation and Rugosity in Vibrio vulnificus.mBio. 2018 Aug 28;9(4):e01377-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01377-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30154262 Free PMC article.
-
Peculiarities of biofilm formation by Paracoccus denitrificans.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Mar;104(6):2427-2433. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10400-w. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32002601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex regulatory networks of virulence factors in Vibrio vulnificus.Trends Microbiol. 2022 Dec;30(12):1205-1216. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2022.05.009. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Trends Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35753865 Review.
Cited by
-
Stimulation of Surface Polysaccharide Production under Aerobic Conditions Confers Aerotolerance in Campylobacter jejuni.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(2):e0376122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03761-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36786626 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA Chaperone Hfq Is Involved in Colony Morphology, Nutrient Utilization and Oxidative and Envelope Stress Response in Vibrio alginolyticus.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 29;11(9):e0163689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163689. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27685640 Free PMC article.
-
FrzS regulates social motility in Myxococcus xanthus by controlling exopolysaccharide production.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023920. Epub 2011 Aug 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21886839 Free PMC article.
-
A Master Regulator BrpR Coordinates the Expression of Multiple Loci for Robust Biofilm and Rugose Colony Development in Vibrio vulnificus.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 25;12:679854. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.679854. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34248894 Free PMC article.
-
Spatio-genetically coordinated TPR domain-containing proteins modulate c-di-GMP signaling in Vibrio vulnificus.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jul 16;21(7):e1013353. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013353. eCollection 2025 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40668869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartolome, B., Y. Jubete, E. Martinez, and F. de la Cruz. 1991. Construction and properties of a family of pACYC184-derived cloning vectors compatible with pBR322 and its derivatives. Gene 102:75-78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

