Two atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains induce the production of secreted and membrane-bound mucins to benefit their own growth at the apical surface of human mucin-secreting intestinal HT29-MTX cells
- PMID: 20065027
- PMCID: PMC2825950
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01115-09
Two atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains induce the production of secreted and membrane-bound mucins to benefit their own growth at the apical surface of human mucin-secreting intestinal HT29-MTX cells
Abstract
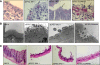
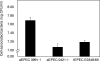
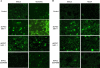
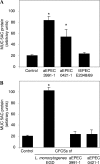
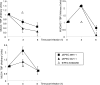
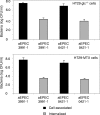
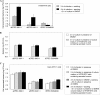
In rabbit ligated ileal loops, two atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (aEPEC) strains, 3991-1 and 0421-1, intimately associated with the cell membrane, forming the characteristic EPEC attachment and effacement lesion of the brush border, induced a mucous hypersecretion, whereas typical EPEC (tEPEC) strain E2348/69 did not. Using cultured human mucin-secreting intestinal HT29-MTX cells, we demonstrate that apically aEPEC infection is followed by increased production of secreted MUC2 and MUC5AC mucins and membrane-bound MUC3 and MUC4 mucins. The transcription of the MUC5AC and MUC4 genes was transiently upregulated after aEPEC infection. We provide evidence that the apically adhering aEPEC cells exploit the mucins' increased production since they grew in the presence of membrane-bound mucins, whereas tEPEC did not. The data described herein report a putative new virulence phenomenon in aEPEC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of a genomic cluster related to hypersecretion of intestinal mucus and mucinolytic activity of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (aEPEC).Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Dec 4;14:1393369. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1393369. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39703371 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the locus of enterocyte effacement genes during the invasion process of the atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli 1711-4 strain of serotype O51:H40.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 3;12(10):e0030424. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00304-24. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39189752 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of atypical enteropathogenic E. coli strains of clinical origin.BMC Microbiol. 2009 Jun 3;9:117. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-117. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19490652 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009 Aug;297(2):137-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01664.x. Epub 2009 May 27. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19527295 Review.
-
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: foe or innocent bystander?Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015 Aug;21(8):729-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.01.015. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015. PMID: 25726041 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nature of bacterial colonization influences transcription of mucin genes in mice during the first week of life.BMC Res Notes. 2012 Aug 2;5:402. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-402. BMC Res Notes. 2012. PMID: 22857743 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Characteristics of Vibrio vulnificus gbpA Gene Encoding a Mucin-binding Protein Essential for Pathogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 11;291(11):5774-5787. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.685321. Epub 2016 Jan 11. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26755724 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of Intestinal Mucin Expression by the Probiotic Bacterium E. coli Nissle 1917.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2012 Jun;4(2):67-77. doi: 10.1007/s12602-012-9092-0. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2012. PMID: 26781849
-
The immunology of the vermiform appendix: a review of the literature.Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 Oct;186(1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/cei.12821. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27271818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct Interaction of Two Atypical Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Strains with Enterocytes In Vitro.Open Microbiol J. 2011;5:65-71. doi: 10.2174/1874285801105010065. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Open Microbiol J. 2011. PMID: 21792379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bara, J., E. Chastre, J. Mahiou, R. L. Singh, M. E. Forgue-Lafitte, E. Hollande, and F. Godeau. 1998. Gastric M1 mucin, an early oncofetal marker of colon carcinogenesis, is encoded by the MUC5AC gene. Int. J. Cancer 75:767-773. - PubMed
-
- Byrd, J. C., C. K. Yunker, Q. S. Xu, L. R. Sternberg, and R. S. Bresalier. 2000. Inhibition of gastric mucin synthesis by Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 118:1072-1079. - PubMed
-
- Caron, E., V. F. Crepin, N. Simpson, S. Knutton, J. Garmendia, and G. Frankel. 2006. Subversion of actin dynamics by EPEC and EHEC. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9:40-45. - PubMed
-
- Chantret, I., A. Rodolosse, A. Barbat, E. Dussaulx, E. Brot-Laroche, A. Zweibaum, and M. Rousset. 1994. Differential expression of sucrase-isomaltase in clones isolated from early and late passages of the cell line Caco-2: evidence for glucose-dependent negative regulation. J. Cell Sci. 107:213-225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

