Protein phosphatase 6 interacts with the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit and dephosphorylates gamma-H2AX
- PMID: 20065038
- PMCID: PMC2832507
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00741-09
Protein phosphatase 6 interacts with the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit and dephosphorylates gamma-H2AX
Abstract
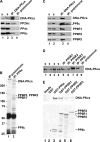
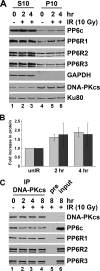
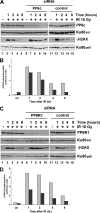
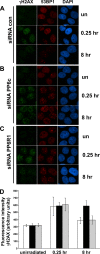
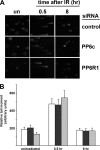
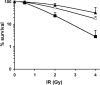
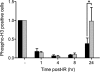
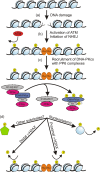
The catalytic subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PKcs) plays a major role in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) by nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ). We have previously shown that DNA-PKcs is autophosphorylated in response to ionizing radiation (IR) and that dephosphorylation by a protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A)-like protein phosphatase (PP2A, PP4, or PP6) regulates the protein kinase activity of DNA-PKcs. Here we report that DNA-PKcs interacts with the catalytic subunits of PP6 (PP6c) and PP2A (PP2Ac), as well as with the PP6 regulatory subunits PP6R1, PP6R2, and PP6R3. Consistent with a role in the DNA damage response, silencing of PP6c by small interfering RNA (siRNA) induced sensitivity to IR and delayed release from the G(2)/M checkpoint. Furthermore, siRNA silencing of either PP6c or PP6R1 led to sustained phosphorylation of histone H2AX on serine 139 (gamma-H2AX) after IR. In contrast, silencing of PP6c did not affect the autophosphorylation of DNA-PKcs on serine 2056 or that of the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) protein on serine 1981. We propose that a novel function of DNA-PKcs is to recruit PP6 to sites of DNA damage and that PP6 contributes to the dephosphorylation of gamma-H2AX, the dissolution of IR-induced foci, and release from the G(2)/M checkpoint in vivo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 dephosphorylates histone variant gamma-H2AX and suppresses DNA double strand break repair.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 23;285(17):12935-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.071696. Epub 2010 Jan 29. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20118229 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-PKcs plays a dominant role in the regulation of H2AX phosphorylation in response to DNA damage and cell cycle progression.BMC Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 6;11:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-18. BMC Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20205745 Free PMC article.
-
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) and protein phosphatase 6 (PP6) regulate DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) phosphorylation in mitosis.Biosci Rep. 2014 Jun 25;34(3):e00113. doi: 10.1042/BSR20140051. Biosci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24844881 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of heterochromatin on DNA double strand break repair: Getting the strong, silent type to relax.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Dec 10;9(12):1273-82. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Oct 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 21036673 Review.
-
Focusing on foci: H2AX and the recruitment of DNA-damage response factors.Cell Cycle. 2003 Sep-Oct;2(5):426-7. Cell Cycle. 2003. PMID: 12963833 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Protein Ser/Thr phosphatase-6 is required for maintenance of E-cadherin at adherens junctions.BMC Cell Biol. 2013 Sep 25;14:42. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-14-42. BMC Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24063632 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of DNA damage response proteins at DNA breaks: a focus on protein modifications.Genes Dev. 2011 Mar 1;25(5):409-33. doi: 10.1101/gad.2021311. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21363960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic K-RasG12V cannot overcome proliferation failure caused by loss of Ppp6c in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.FEBS Open Bio. 2024 Apr;14(4):545-554. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13775. Epub 2024 Feb 6. FEBS Open Bio. 2024. PMID: 38318686 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted roles of Arabidopsis PP6 phosphatase in regulating cellular signaling and plant development.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Jan;8(1):e22508. doi: 10.4161/psb.22508. Epub 2012 Oct 26. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23104112 Free PMC article.
-
Push back to respond better: regulatory inhibition of the DNA double-strand break response.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;14(10):661-72. doi: 10.1038/nrm3659. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24002223 Review.
References
-
- Achari, Y., and S. P. Lees-Miller. 2000. Detection of DNA-dependent protein kinase in extracts from human and rodent cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 99:85-97. - PubMed
-
- Ahnesorg, P., P. Smith, and S. P. Jackson. 2006. XLF interacts with the XRCC4-DNA ligase IV complex to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Cell 124:301-313. - PubMed
-
- Allalunis-Turner, M. J., P. K. Zia, G. M. Barron, R. Mirzayans, and R. S. Day III. 1995. Radiation-induced DNA damage and repair in cells of a radiosensitive human malignant glioma cell line. Radiat. Res. 144:288-293. - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist, C. J., and M. B. Kastan. 2003. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature 421:499-506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
