Attenuation of cerebrospinal fluid inflammation by the nonbacteriolytic antibiotic daptomycin versus that by ceftriaxone in experimental pneumococcal meningitis
- PMID: 20065062
- PMCID: PMC2825988
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00812-09
Attenuation of cerebrospinal fluid inflammation by the nonbacteriolytic antibiotic daptomycin versus that by ceftriaxone in experimental pneumococcal meningitis
Abstract
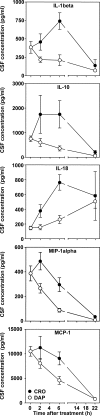
Antibiotic-induced bacteriolysis exacerbates inflammation and brain damage in bacterial meningitis. Here the quality and temporal kinetics of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inflammation were assessed in an infant rat pneumococcal meningitis model for the nonbacteriolytic antibiotic daptomycin versus ceftriaxone. Daptomycin led to lower CSF concentrations of interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta), IL-10, IL-18, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), and macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha (MIP-1alpha) (P < 0.05). In experimental pneumococcal meningitis, daptomycin treatment resulted in more rapid bacterial killing, lower CSF inflammation, and less brain damage than ceftriaxone treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adjunctive daptomycin attenuates brain damage and hearing loss more efficiently than rifampin in infant rat pneumococcal meningitis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Aug;56(8):4289-95. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00674-12. Epub 2012 May 29. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22644021 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of brain injury by the nonbacteriolytic antibiotic daptomycin in experimental pneumococcal meningitis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jun;51(6):2173-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01014-06. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17371820 Free PMC article.
-
Daptomycin produces an enhanced bactericidal activity compared to ceftriaxone, measured by [3H]choline release in the cerebrospinal fluid, in experimental meningitis due to a penicillin-resistant pneumococcal strain without lysing its cell wall.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jun;51(6):2249-52. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01000-06. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17371817 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of pneumococcal meningitis.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Jul;24(3):557-91. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00008-11. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21734248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adjunctive treatments for pneumococcal meningitis: a systematic review of experimental animal models.Brain Commun. 2024 Apr 12;6(3):fcae131. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae131. eCollection 2024. Brain Commun. 2024. PMID: 38707710 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metformin mediates neuroprotection and attenuates hearing loss in experimental pneumococcal meningitis.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Jul 27;16(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1549-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31351490 Free PMC article.
-
Combined effect of non-bacteriolytic antibiotic and inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases prevents brain injury and preserves learning, memory and hearing function in experimental paediatric pneumococcal meningitis.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Aug 21;15(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1272-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30131074 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Pharmaceutical Approaches of Antimicrobial Agents for Selective Delivery in Various Administration Routes.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;12(5):822. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12050822. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Nanoconjugate of Apamin and Ceftriaxone for Management of Diabetic Wounds.Life (Basel). 2022 Jul 21;12(7):1096. doi: 10.3390/life12071096. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35888184 Free PMC article.
-
Do different anesthesia regimes affect hippocampal apoptosis and neurologic deficits in a rodent cardiac arrest model?BMC Anesthesiol. 2015 Jan 15;15:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2253-15-2. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015. PMID: 25972075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baltz, R. H. 2009. Daptomycin: mechanisms of action and resistance, and biosynthetic engineering. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 13:144-151. - PubMed
-
- Bifrare, Y. D., C. Gianinazzi, H. Imboden, S. L. Leib, and M. G. Täuber. 2003. Bacterial meningitis causes two distinct forms of cellular damage in the hippocampal dentate gyrus in infant rats. Hippocampus 13:481-488. - PubMed
-
- Cottagnoud, P., M. Pfister, F. Acosta, M. Cottagnoud, L. Flatz, F. Kuhn, H. P. Muller, and A. Stucki. 2004. Daptomycin is highly efficacious against penicillin-resistant and penicillin- and quinolone-resistant pneumococci in experimental meningitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:3928-3933. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Egermann, U., Z. Stanga, A. Ramin, F. Acosta, A. Stucki, P. Gerber, M. Cottagnoud, and P. Cottagnoud. 2009. The combination of daptomycin plus ceftriaxone was more active than vancomycin plus ceftriaxone in experimental meningitis after addition of dexamethasone. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53:3030-3033. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gehre, F., S. L. Leib, D. Grandgirard, J. Kummer, A. Bühlmann, F. Simon, R. Gäumann, A. S. Kharat, M. G. Täuber, and A. Tomasz. 2008. Essential role of choline for pneumococcal virulence in an experimental model of meningitis. J. Intern. Med. 264:143-154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

