Genetic and pharmacological targeting of activin receptor-like kinase 1 impairs tumor growth and angiogenesis
- PMID: 20065063
- PMCID: PMC2812548
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20091309
Genetic and pharmacological targeting of activin receptor-like kinase 1 impairs tumor growth and angiogenesis
Abstract
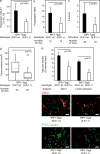
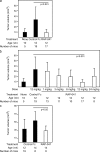
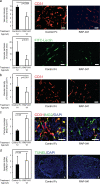
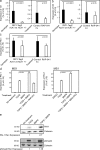
Members of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) family have been genetically linked to vascular formation during embryogenesis. However, contradictory studies about the role of TGF-beta and other family members with reported vascular functions, such as bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 9, in physiological and pathological angiogenesis make the need for mechanistic studies apparent. We demonstrate, by genetic and pharmacological means, that the TGF-beta and BMP9 receptor activin receptor-like kinase (ALK) 1 represents a new therapeutic target for tumor angiogenesis. Diminution of ALK1 gene dosage or systemic treatment with the ALK1-Fc fusion protein RAP-041 retarded tumor growth and progression by inhibition of angiogenesis in a transgenic mouse model of multistep tumorigenesis. Furthermore, RAP-041 significantly impaired the in vitro and in vivo angiogenic response toward vascular endothelial growth factor A and basic fibroblast growth factor. In seeking the mechanism for the observed effects, we uncovered an unexpected signaling synergy between TGF-beta and BMP9, through which the combined action of the two factors augmented the endothelial cell response to angiogenic stimuli. We delineate a decisive role for signaling by TGF-beta family members in tumor angiogenesis and offer mechanistic insight for the forthcoming clinical development of drugs blocking ALK1 in oncology.
Figures



References
-
- Arthur H.M., Ure J., Smith A.J., Renforth G., Wilson D.I., Torsney E., Charlton R., Parums D.V., Jowett T., Marchuk D.A., et al. 2000. Endoglin, an ancillary TGFβ receptor, is required for extraembryonic angiogenesis and plays a key role in heart development. Dev. Biol. 217:42–53 10.1006/dbio.1999.9534 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

