Control of chemical effects in the separation process of a differential mobility mass spectrometer system
- PMID: 20065515
- PMCID: PMC3672227
- DOI: 10.1255/ejms.1025
Control of chemical effects in the separation process of a differential mobility mass spectrometer system
Abstract
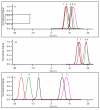
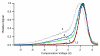
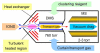
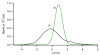
Differential mobility spectrometry (DMS) separates ions on the basis of the difference in their migration rates under high versus low electric fields. Several models describing the physical nature of this field mobility dependence have been proposed but emerging as a dominant effect is the clusterization model sometimes referred to as the dynamic cluster-decluster model. DMS resolution and peak capacity is strongly influenced by the addition of modifiers which results in the formation and dissociation of clusters. This process increases selectivity due to the unique chemical interactions that occur between an ion and neutral gas-phase molecules. It is thus imperative to bring the parameters influencing the chemical interactions under control and find ways to exploit them in order to improve the analytical utility of the device. In this paper, we describe three important areas that need consideration in order to stabilize and capitalize on the chemical processes that dominate a DMS separation. The first involves means of controlling the dynamic equilibrium of the clustering reactions with high concentrations of specific reagents. The second area involves a means to deal with the unwanted heterogeneous cluster ion populations emitted from the electrospray ionization process that degrade resolution and sensitivity. The third involves fine control of parameters that affect the fundamental collision processes, temperature and pressure.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Description of gas-phase ion/neutral interactions in differential ion mobility spectrometry: CV prediction using calibration runs.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014 Sep;25(9):1610-21. doi: 10.1007/s13361-014-0934-8. Epub 2014 Jun 14. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014. PMID: 24927778
-
Chemical effects in the separation process of a differential mobility/mass spectrometer system.Anal Chem. 2010 Mar 1;82(5):1867-80. doi: 10.1021/ac902571u. Anal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20121077 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid separation and quantitative analysis of peptides using a new nanoelectrospray- differential mobility spectrometer-mass spectrometer system.Anal Chem. 2006 Aug 1;78(15):5443-52. doi: 10.1021/ac060003f. Anal Chem. 2006. PMID: 16878881
-
Ion mobility-mass spectrometry.J Mass Spectrom. 2008 Jan;43(1):1-22. doi: 10.1002/jms.1383. J Mass Spectrom. 2008. PMID: 18200615 Review.
-
High-field asymmetric waveform ion mobility spectrometry for mass spectrometry-based proteomics.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2012 Oct;9(5):505-17. doi: 10.1586/epr.12.50. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 23194268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preferential Ion Microsolvation in Mixed-Modifier Environments Observed Using Differential Mobility Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019 Nov;30(11):2222-2227. doi: 10.1007/s13361-019-02332-1. Epub 2019 Sep 16. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019. PMID: 31529402
-
Description of gas-phase ion/neutral interactions in differential ion mobility spectrometry: CV prediction using calibration runs.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014 Sep;25(9):1610-21. doi: 10.1007/s13361-014-0934-8. Epub 2014 Jun 14. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014. PMID: 24927778
-
High-definition differential ion mobility spectrometry with resolving power up to 500.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013 Jan;24(1):109-14. doi: 10.1007/s13361-012-0517-5. Epub 2012 Dec 20. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013. PMID: 23345059 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing Glycopeptide Isomers by Combining Differential Mobility Spectrometry with Electron- and Collision-Based Tandem Mass Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2017 Jul;28(7):1374-1381. doi: 10.1007/s13361-017-1663-6. Epub 2017 Apr 21. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2017. PMID: 28432653
-
Determination of Collisional Cross Section Using Microscale High-Field Asymmetric Waveform ion Mobility Spectroscopy-Mass Spectrometry (FAIMS-MS).Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2025 May 30;39(10):e10010. doi: 10.1002/rcm.10010. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2025. PMID: 39962628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eiceman G, Karpas Z. Ion Mobility Spectrometry. 2nd ed. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis LLC; Boca Raton, FL: 2005.
-
- Krylov EV, Nazarov EG, Miller RA. Differential mobility spectrometer: Model of operation. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007;226:76.
-
- Shvartsburg A. Differential Ion Mobility: Non-Linear Ion Transport and Fundamentals of FAIMS. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis LLC; Boca Raton, FL: 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

