Monoclonal antibodies and other biologic agents in the treatment of asthma
- PMID: 20065638
- PMCID: PMC2726591
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.1.3.8352
Monoclonal antibodies and other biologic agents in the treatment of asthma
Abstract
Asthma represents a syndrome of airway inflammatory diseases with complex pathology. The immunologic pathogenesis is being increasingly revealed and provides opportunity for targeted biological intervention. Current experience with immunomodulators as targeted therapy in asthma is described in this literature review. Targeted therapies have included strategies to activate dendritic cells through the TLR-9 receptors, to interrupt the action of T(H)2 cytokines with cytokine blockers and monoclonal antibodies, to promote development of T(H)1 responses, to block IgE mediated pathways and to block TNFalpha. Omalizumab is the only biological therapy that has an approved indication in asthma at this time. An improved understanding of the heterogeneity of asthma should allow for specific targeting of different disease phenotypes specific therapies including immunomodulators.
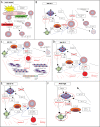
Figures

References
-
- Busse WW, Lemanske R., Jr Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:350–362. - PubMed
-
- Pascual RM, Peters SP. Airway remodeling contributes to the progressive loss of lung function in asthma: an overview. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;116:477–486. - PubMed
-
- Holgate ST, Polosa R. Treatment strategies for allergy and asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:218–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
