The urine proteome for radiation biodosimetry: effect of total body vs. local kidney irradiation
- PMID: 20065682
- PMCID: PMC2920640
- DOI: 10.1097/HP.0b013e3181b17cbd
The urine proteome for radiation biodosimetry: effect of total body vs. local kidney irradiation
Abstract
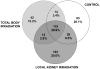
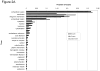
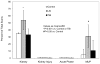
Victims of nuclear accidents or radiological terrorism are likely to receive varying doses of ionizing radiation inhomogeneously distributed over the body. Early biomarkers may be useful in determining organ-specific doses due to total body irradiation (TBI) or partial body irradiation. The authors used liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry to compare the effect of TBI and local kidney irradiation (LKI) on the rat urine proteome using a single 10-Gy dose of x-rays. Both TBI and LKI altered the urinary protein profile within 24 h with noticeable differences in gene ontology categories. Some proteins, including fetuin-B, tissue kallikrein, beta-glucuronidase, vitamin D-dependent calcium binding protein and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan NG2, were detected only in the TBI group. Some other proteins, including major urinary protein-1, RNA binding protein 19, neuron navigator, Dapper homolog 3, WD repeat and FYVE domain containing protein 3, sorting nexin-8, ankycorbin and aquaporin were detected only in the LKI group. Protease inhibitors and kidney proteins were more abundant (fraction of total scans) in the LKI group. Urine protein (Up) and creatinine (Uc) (Up/Uc) ratios and urinary albumin abundance decreased in both TBI and LKI groups. Several markers of acute kidney injury were not detectable in either irradiated group. Present data indicate that abundance and number of proteins may follow opposite trends. These novel findings demonstrate intriguing differences between TBI and LKI, and suggest that urine proteome may be useful in determining organ-specific changes caused by partial body irradiation.
Figures


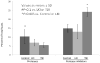
Similar articles
-
The urine proteome as a radiation biodosimeter.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;990:87-100. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5896-4_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23378004 Review.
-
Identifying Urinary and Serum Exosome Biomarkers for Radiation Exposure Using a Data Dependent Acquisition and SWATH-MS Combined Workflow.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016 Nov 1;96(3):566-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.06.008. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016. PMID: 27485285 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple parameter radiation injury assessment using a nonhuman primate radiation model-biodosimetry applications.Health Phys. 2010 Feb;98(2):153-9. doi: 10.1097/HP.0b013e3181b0306d. Health Phys. 2010. PMID: 20065677
-
Revisiting Biomarkers of Total-Body and Partial-Body Exposure in a Baboon Model of Irradiation.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0132194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132194. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26177207 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Disease in Childhood Cancer Survivors Treated With Radiation Therapy: A PENTEC Comprehensive Review.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024 Jun 1;119(2):560-574. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.02.040. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024. PMID: 37452796 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiation injury treatment network (RITN): healthcare professionals preparing for a mass casualty radiological or nuclear incident.Int J Radiat Biol. 2011 Aug;87(8):748-53. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2011.556176. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011. PMID: 21801106 Free PMC article.
-
Making connections: the scientific impact and mentoring legacy of Dr. John E. Moulder.Int J Radiat Biol. 2023;99(7):1009-1015. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2023.2176563. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Int J Radiat Biol. 2023. PMID: 36763099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a metabolomic radiation signature in urine from patients undergoing total body irradiation.Radiat Res. 2014 Apr;181(4):350-61. doi: 10.1667/RR13567.1. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 24673254 Free PMC article.
-
Candidate gene biodosimetry markers of exposure to external ionizing radiation in human blood: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 7;13(6):e0198851. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198851. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29879226 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of biodosimetry methods for a mass-casualty radiological incident: medical response and management considerations.Health Phys. 2013 Dec;105(6):540-54. doi: 10.1097/HP.0b013e31829cf221. Health Phys. 2013. PMID: 24162058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boschetti E, Giorgio Righetti P. Hexapeptide combinatorial ligand libraries: the march for the detection of the low-abundance proteome continues. Biotech. 2008;44:663–665. - PubMed
-
- Cavaggioni A, Mucignat-Caretta C. Major urinary proteins, alpha(2U)-globulins and aphrodisin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1482:218–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

