Induction of B-cell immune tolerance by antigen-modified cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- PMID: 20065917
- PMCID: PMC2844488
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181ca9048
Induction of B-cell immune tolerance by antigen-modified cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Abstract
Background: Third-party-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), or veto CTL, are being assessed as a cellular therapeutic for the induction of T-cell tolerance during transplantation. Conceptually, veto cell-expressed antigens (Ags) may induce B-cell immune responses, and this may have deleterious consequences. Whether veto cells induce immunity, tolerance, or are ignored by B lymphocytes has, however, not been addressed.
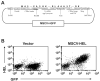
Methods: CTL were retrovirally transduced with a model cell surface Ag to generate veto CTL. The impact of CTL-specific Ag expression on the activation and tolerization of Ag-specific B cells was assessed in vitro and, using adoptive transfer models, in vivo.
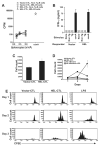
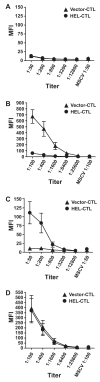
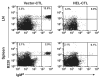
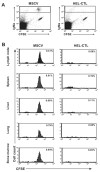
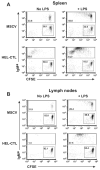
Results: In vitro, CTL-expressed Ag induced an abortive proliferative response in specific B lymphocytes, whereby an initial proliferative burst was followed by cell death. In vivo, the administration of veto CTL also induced B-cell tolerance. Specific immunoglobulin was not detected after subsequent immunization with a veto cell-expressed Ag. Modeling of this effect with Ag-specific B-cell receptor transgenic B lymphocytes demonstrated that Ag-specific B cells were eliminated by the veto CTL; the cell division was accompanied by the exhaustion and depletion of responding cells. Veto-induced B-cell tolerance could be wholly abrogated by treatment with the toll-like receptor ligand lipopolysaccharide, implying that this tolerance resulted from the absence of adequate supplemental signals during antigenic stimulation.
Conclusions: Veto CTL are effective promoters of B-cell tolerance. Further assessment of their therapeutic potential in this regard is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no commercial interests relating to this work.
Figures
Comment in
-
Are B cells agreeable to veto?Transplantation. 2010 Mar 27;89(6):646-7. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181ca9065. Transplantation. 2010. PMID: 20048694 No abstract available.
References
-
- Soiffer R. Immune modulation and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008;42 1:S66–S69. - PubMed
-
- Zarkhin V, Li L, Sarwal M. “To B or not to B?” B-cells and graft rejection. Transplantation. 2008;85:1705–1714. - PubMed
-
- Brennan DC, Mohanakumar T, Flye MW. Donor-specific transfusion and donor bone marrow infusion in renal transplantation tolerance: a review of efficacy and mechanisms. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995;26:701–715. - PubMed
-
- Fabre JW, Morris PJ. The effect of donor strain blood pretreatment on renal allograft rejection in rats. Transplantation. 1972;14:608–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

