Establishing and interpreting graded Sonic Hedgehog signaling during vertebrate neural tube patterning: the role of negative feedback
- PMID: 20066087
- PMCID: PMC2742090
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002014
Establishing and interpreting graded Sonic Hedgehog signaling during vertebrate neural tube patterning: the role of negative feedback
Abstract
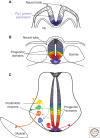
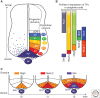
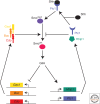
The secreted protein Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) acts in graded fashion to pattern the dorsal-ventral axis of the vertebrate neural tube. This is a dynamic process in which increasing concentrations and durations of exposure to SHH generate neurons with successively more ventral identities. Interactions between the receiving cells and the graded signal underpin the mechanism of SHH action. In particular, negative feedback, involving proteins transcriptionally induced or repressed by SHH signaling, plays an essential role in shaping the graded readout. On one hand, negative feedback controls, in a noncell-autonomous manner, the distribution of SHH across the field of receiving cells. On the other, it acts cell-autonomously to convert different concentrations of SHH into distinct durations of intracellular signal transduction. Together, these mechanisms exemplify a strategy for morphogen interpretation, which we have termed temporal adaptation that relies on the continuous processing and refinement of the cellular response to the graded signal.
Figures
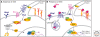

References
-
- Ashe HL, Briscoe J 2006. The interpretation of morphogen gradients. Development 133:385–394 - PubMed
-
- Aza-Blanc P, Lin HY, Ruiz i Altaba A, Kornberg TB 2000. Expression of the vertebrate Gli proteins in Drosophila reveals a distribution of activator and repressor activities. Development 127:4293–4301 - PubMed
-
- Bai CB, Stephen D, Joyner AL 2004. All mouse ventral spinal cord patterning by hedgehog is Gli dependent and involves an activator function of Gli3. Dev Cell 6:103–115 - PubMed
-
- Bailey PJ, Klos JM, Andersson E, Karlen M, Kallstrom M, Ponjavic J, Muhr J, Lenhard B, Sandelin A, Ericson J 2006. A global genomic transcriptional code associated with CNS-expressed genes. Exp Cell Res 312:3108–3119 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
