Physiology and function of the tight junction
- PMID: 20066090
- PMCID: PMC2742087
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002584
Physiology and function of the tight junction
Abstract
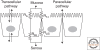
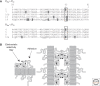
Understanding of tight junctions has evolved from their historical perception as inert solute barriers to recognition of their physiological and biochemical complexity. Many proteins are specifically localized to tight junctions, including cytoplasmic actin-binding proteins and adhesive transmembrane proteins. Among the latter are claudins, which are critical barrier proteins. Current information suggests that the paracellular barrier is most usefully modeled as having two physiologic components: a system of charge-selective small pores, 4 A in radius, and a second pathway created by larger discontinuities in the barrier, lacking charge or size discrimination. The first pathway is influenced by claudin expression patterns and the second is likely controlled by different proteins and signals. Recent information on claudin function and disease-causing mutations have led to a more complete understanding of their role in barrier formation, but progress is impeded by lack of high resolution structural information.
Figures

References
-
- Alexandre MD, Lu Q, Chen YH 2005. Overexpression of claudin-7 decreases the paracellular Cl− conductance and increases the paracellular Na+ conductance in LLC-PK1 cells. J Cell Sci 118:2683–2693 - PubMed
-
- Amasheh S, Meiri N, Gitter AH, Schoneberg T, Mankertz J, Schulzke JD, Fromm M 2002. Claudin-2 expression induces cation-selective channels in tight junctions of epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 115:4969–4976 - PubMed
-
- Amasheh S, Schmidt T, Mahn M, Florian P, Mankertz J, Tavalali S, Gitter AH, Schulzke JD, Fromm M 2005. Contribution of claudin-5 to barrier properties in tight junctions of epithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res 321:89–96 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
