Management of asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis
- PMID: 20066145
- PMCID: PMC2803285
- DOI: 10.2174/157340309787048103
Management of asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis
Abstract
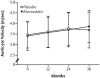
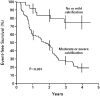
Patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis (AS) benefit from aortic valve replacement surgery, but the management of patients with asymptomatic severe AS is more controversial. While cholesterol and angiotensin have been linked to AS progression, we should await the results of ongoing randomized trials before medical therapy to lower cholesterol or inhibit angiotensin can be recommended to limit disease progression. Clinical factors, echocardiographic parameters, valve morphology, exercise stress testing results, and cardiac biomarkers may be useful in identifying patients who will have early development of symptoms during follow-up and require closer monitoring. The risks associated with aortic valve replacement outweigh the benefits in the majority of patients with asymptomatic severe AS.
Keywords: Aortic valve stenosis; brain natriuretic peptide.; exercise testing; management; surgery; symptoms.
Figures
References
-
- Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Chattejee K, et al. ACC/AHA 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease. A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:e1–148. - PubMed
-
- Otto CM, Burwash IG, Legget ME, et al. Prospective study of asymptomatic valvular aortic stenosis: clinical, echocardiographic, and exercise predictors of outcome. Circulation. 1997;95:2262–70. - PubMed
-
- Ross J Jr, Braunwald E. Aortic stenosis. Circulation. 1968;38(suppl 5):561–7. - PubMed
-
- Horstkotte D, Loogen F. The natural history of aortic valve stenosis. Eur Heart J. 1988;9(suppl E):57–64. - PubMed
-
- Rosenhek R, Binder T, Porenta G, et al. Predictors of outcome in severe, asymptomatic aortic stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:611–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

