Treatment of biliary tract cancer with NVP-AEW541: mechanisms of action and resistance
- PMID: 20066734
- PMCID: PMC2806553
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i2.156
Treatment of biliary tract cancer with NVP-AEW541: mechanisms of action and resistance
Abstract
Aim: To investigate in vitro treatment with NVP-AEW541, a small molecule inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), in biliary tract cancer (BTC), since this disease is associated with a poor prognosis due to wide resistance to chemotherapeutic agents and radiotherapy.
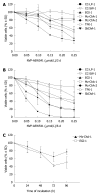
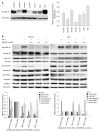
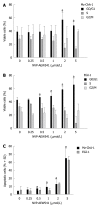
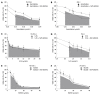
Methods: Cell growth inhibition by NVP-AEW541 was studied in vitro in 7 human BTC cell lines by automated cell counting. In addition, the anti-tumoral mechanism of NVP-AEW541 was studied by Western blotting, cell cycle analysis and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Anti-tumoral drug effect in combination with gemcitabine, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor BI2536 was also studied.
Results: In vitro treatment with NVP-AEW541 suppressed growth in all human BTC cell lines, however response was lower in gallbladder cancer. Treatment with NVP-AEW541 was associated with dephosphorylation of IGF-1R and AKT. In contrast, phosphorylation of p42/p44 and Stat3 and expression of Bcl-xL were inconsistently downregulated. In addition, treated cells showed cell cycle arrest at the G1/S-checkpoint and an increase in sub-G1 peak. Moreover, IGF-1R and its ligands IGF-1 and IGF-2 were co-expressed in RT-PCR, suggesting an autocrine loop of tumor cell activation. Combined with gemcitabine, NVP-AEW541 exerted synergistic effects, particularly at low concentrations, while effects of combination with 5-FU or BI 2536 were only additive.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that NVP-AEW541 is active against BTC in vitro and potentiates the efficacy of gemcitabine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of insulin-like growth factor I receptor activity by NVP-AEW541 has an antitumor effect on neuroblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Nov 15;12(22):6772-80. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1479. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17121898
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition as a new therapeutic modality in therapy of cholangiocarcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2011 Oct;31(10):3289-99. Anticancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21965739
-
Blockade of IGF-1 receptor tyrosine kinase has antineoplastic effects in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 May 14;71(10):1435-48. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.02.006. Epub 2006 Mar 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16530734
-
Targeting P53 as a Future Strategy to Overcome Gemcitabine Resistance in Biliary Tract Cancers.Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 23;10(11):1474. doi: 10.3390/biom10111474. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33113997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting phosphoinositide-3-kinase pathway in biliary tract cancers: A remedial route?J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):8259-8273. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27673. Epub 2018 Oct 28. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30370571 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF-1R) signaling systems: novel treatment strategies for cancer.Med Oncol. 2014 Jan;31(1):805. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0805-3. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24338270 Review.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor-induced mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor activation leads to insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor unresponsiveness in gastric cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Nov;16(5):5983-5991. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9414. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30333869 Free PMC article.
-
IGF-I signaling is essential for FSH stimulation of AKT and steroidogenic genes in granulosa cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Mar;27(3):511-23. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1307. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23340251 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor system in cancer: novel targeted therapies.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:538019. doi: 10.1155/2015/538019. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25866791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-regulation of IGF-1R expression inhibits growth and enhances chemosensitivity of endometrial carcinoma in vitro.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Jul;353(1-2):225-33. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0790-9. Epub 2011 Mar 26. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21442237
References
-
- Ullrich A, Gray A, Tam AW, Yang-Feng T, Tsubokawa M, Collins C, Henzel W, Le Bon T, Kathuria S, Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986;5:2503–2512. - PMC - PubMed
-
- White MF, Kahn CR. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Myers MG Jr, Sun XJ, Cheatham B, Jachna BR, Glasheen EM, Backer JM, White MF. IRS-1 is a common element in insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I signaling to the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase. Endocrinology. 1993;132:1421–1430. - PubMed
-
- Baserga R. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as a target for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2005;9:753–768. - PubMed
-
- Sachdev D, Yee D. Disrupting insulin-like growth factor signaling as a potential cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

