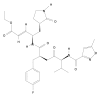
Rupintrivir is a promising candidate for treating severe cases of Enterovirus-71 infection
- PMID: 20066739
- PMCID: PMC2806558
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i2.201
Rupintrivir is a promising candidate for treating severe cases of Enterovirus-71 infection
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the suitability of rupintrivir against Enterovirus 71 (EV71) induced severe clinical symptoms using computational methods.
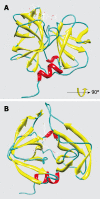
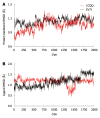
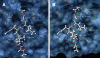
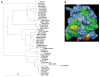
Methods: The structure of EV71 3C protease was predicted by homology modeling. The binding free energies between rupintrivir and EV71 3C and human rhinovirus 3C protease were computed by molecular dynamics and molecular mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann/surface area and molecular mechanics generalized-born/surface area methods. EV71 3C fragments obtained from clinical samples collected during May to July 2008 in Shanghai were amplified by reverse-transcription and polymerase chain reaction and sequenced.
Results: We observed that rupintrivir had favorable binding affinity with EV71 3C protease (-10.76 kcal/mol). The variability of the 3C protein sequence in isolates of various outbreaks, including those obtained in our hospital from May to July 2008, were also analyzed to validate the conservation of the drug binding pocket.
Conclusion: Rupintrivir, whose safety profiles had been proved, is an attractive candidate and can be quickly utilized for treating severe EV71 infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Crystal structures of enterovirus 71 3C protease complexed with rupintrivir reveal the roles of catalytically important residues.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(19):10021-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05107-11. Epub 2011 Aug 3. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21813612 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidomimetic ethyl propenoate covalent inhibitors of the enterovirus 71 3C protease: a P2-P4 study.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016;31(2):332-9. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2015.1018245. Epub 2015 Sep 4. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 25792507
-
Enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 3C proteases: binding to rupintrivir and their substrates and anti-hand, foot, and mouth disease virus drug design.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(19):10319-31. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00787-11. Epub 2011 Jul 27. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21795339 Free PMC article.
-
The Function and Mechanism of Enterovirus 71 (EV71) 3C Protease.Curr Microbiol. 2020 Sep;77(9):1968-1975. doi: 10.1007/s00284-020-02082-4. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Curr Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32556480 Review.
-
The treatment of rhinovirus infections: progress and potential.Antiviral Res. 2001 Jan;49(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(00)00135-2. Antiviral Res. 2001. PMID: 11166856 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of enterovirus 71 replication and viral 3C protease by quercetin.Virol J. 2018 Jul 31;15(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12985-018-1023-6. Virol J. 2018. PMID: 30064445 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of enterovirus 71 3C protease complexed with rupintrivir reveal the roles of catalytically important residues.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(19):10021-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05107-11. Epub 2011 Aug 3. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21813612 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Plasmid DNA-Based Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Minigenome for Intracytoplasmic mRNA Production.Viruses. 2021 Jun 1;13(6):1047. doi: 10.3390/v13061047. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34205958 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of human enterovirus 71 3C protease.J Mol Biol. 2011 May 6;408(3):449-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.03.007. Epub 2011 Mar 17. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21396941 Free PMC article.
-
Improved synthesis of rupintrivir.Sci China Chem. 2012;55(6):1101-1107. doi: 10.1007/s11426-011-4478-5. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Sci China Chem. 2012. PMID: 32215000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kräusslich HG, Nicklin MJ, Lee CK, Wimmer E. Polyprotein processing in picornavirus replication. Biochimie. 1988;70:119–130. - PubMed
-
- Leong LE, Walker PA, Porter AG. Human rhinovirus-14 protease 3C (3Cpro) binds specifically to the 5’-noncoding region of the viral RNA. Evidence that 3Cpro has different domains for the RNA binding and proteolytic activities. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:25735–25739. - PubMed
-
- Lee ES, Lee WG, Yun SH, Rho SH, Im I, Yang ST, Sellamuthu S, Lee YJ, Kwon SJ, Park OK, et al. Development of potent inhibitors of the coxsackievirus 3C protease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;358:7–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

