VEGF165 promotes the osteolytic bone destruction of ewing's sarcoma tumors by upregulating RANKL
- PMID: 20066901
- PMCID: PMC2875875
- DOI: 10.3727/096504009789954627
VEGF165 promotes the osteolytic bone destruction of ewing's sarcoma tumors by upregulating RANKL
Abstract
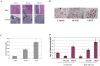
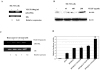
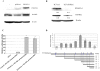
The purpose of this study was to determine whether vascular endothelial growth factor-165 (VEGF165) contributed to the osteolytic process in Ewing's sarcoma. VEGF165 induced osteoclast formation from murine bone marrow cells. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining demonstrated significantly fewer osteoclasts in VEGF-inhibited TC/siVEGF7-1 tumors compared to TC71 parental or TC/si-control tumors. Receptor activator NF-kappaB (RANKL), a critical osteoclastogenic factor, was decreased in TC/siVEGF7-1 cells. Incubation of these cells with recombinant VEGF165 upregulated RANKL in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The induction of (RANKL) by VEGF165 was also demonstrated in MC3T3-E1 mouse osteoblast cells and bone marrow stromal cells. This upregulation was transcriptionally mediated by an effect on the RANKL promoter. Both VEGF and EWS/FLI-1 increased RANKL promoter activity. Taken together, these data suggest that modulation of RANKL by VEGF165 may be one of the mechanisms responsible for the osteolytic process induced by Ewing's sarcoma cells. VEGF165 may, therefore, play an important role in modulating RANKL gene expression in the bone marrow microenvironment during the metastatic process, thereby contribution to tumor induced bone lysis.
Figures

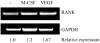
Similar articles
-
Cellular and humoral mechanisms of osteoclast formation in Ewing's sarcoma.Br J Cancer. 2007 Jun 4;96(11):1716-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603774. Epub 2007 May 29. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17533390 Free PMC article.
-
Production of VEGF165 by Ewing's sarcoma cells induces vasculogenesis and the incorporation of CD34+ stem cells into the expanding tumor vasculature.Int J Cancer. 2006 Aug 15;119(4):839-46. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21916. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16557578
-
A small interfering RNA targeting vascular endothelial growth factor inhibits Ewing's sarcoma growth in a xenograft mouse model.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Apr 1;11(7):2662-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1206. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15814647
-
Promiscuous partnerships in Ewing's sarcoma.Cancer Genet. 2011 Jul;204(7):351-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2011.07.008. Cancer Genet. 2011. PMID: 21872822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights in myeloma-induced osteolysis.Leuk Lymphoma. 2003 Sep;44(9):1463-7. doi: 10.3109/10428190309178765. Leuk Lymphoma. 2003. PMID: 14565645 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting VEGF and Its Receptors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis and Associated Pain.J Bone Miner Res. 2016 May;31(5):911-24. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2828. Epub 2016 Apr 8. J Bone Miner Res. 2016. PMID: 27163679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of VEGFs/VEGFR-1 Signaling and its Inhibition in Modulating Tumor Invasion: Experimental Evidence in Different Metastatic Cancer Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 18;21(4):1388. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041388. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32085654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone sarcomas: from biology to targeted therapies.Sarcoma. 2012;2012:301975. doi: 10.1155/2012/301975. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Sarcoma. 2012. PMID: 23226965 Free PMC article.
-
High Potency VEGFRs/MET/FMS Triple Blockade by TAS-115 Concomitantly Suppresses Tumor Progression and Bone Destruction in Tumor-Induced Bone Disease Model with Lung Carcinoma Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 13;11(10):e0164830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164830. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27736957 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage infiltration predicts a poor prognosis for human ewing sarcoma.Am J Pathol. 2011 Sep;179(3):1157-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.05.034. Epub 2011 Jul 21. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21771572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riggi N, Stamenkovic I. The Biology of Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Lett. 2007;254:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Galindo C, Spunt SL, Pappo AS. Treatment of Ewing sarcoma family of tumors: current status and outlook for the future. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003;40:276–287. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak HF. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4368–4380. - PubMed
-
- Lee TH, Bolontrade MF, Worth LL, Guan H, Ellis LM, Kleinerman ES. Production of VEGF165 by Ewing's sarcoma cells induces vasculogenesis and the incorporation of CD34+ stem cells into the expanding tumor vasculature. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:839–846. - PubMed
-
- Guan H, Zhou Z, Wang H, Jia SF, Liu W, Kleinerman ES. A small interfering RNA targeting vascular endothelial growth factor inhibits Ewing's sarcoma growth in a xenograft mouse model. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2662–2669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
