Design and synthesis of novel quinone inhibitors targeted to the redox function of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox enhancing factor-1 (Ape1/ref-1)
- PMID: 20067291
- PMCID: PMC2834202
- DOI: 10.1021/jm9014857
Design and synthesis of novel quinone inhibitors targeted to the redox function of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox enhancing factor-1 (Ape1/ref-1)
Abstract
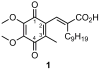
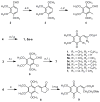
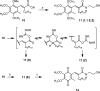
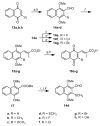
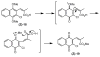
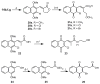
The multifunctional enzyme apurinic endonuclease 1/redox enhancing factor 1 (Ape1/ref-1) maintains genetic fidelity through the repair of apurinic sites and regulates transcription through redox-dependent activation of transcription factors. Ape1 can therefore serve as a therapeutic target in either a DNA repair or transcriptional context. Inhibitors of the redox function can be used as either therapeutics or novel tools for separating the two functions for in vitro study. Presently there exist only a few compounds that have been reported to inhibit Ape1 redox activity; here we describe a series of quinones that exhibit micromolar inhibition of the redox function of Ape1. Benzoquinone and naphthoquinone analogues of the Ape1-inhibitor E3330 were designed and synthesized to explore structural effects on redox function and inhibition of cell growth. Most of the naphthoquinones were low micromolar inhibitors of Ape1 redox activity, and the most potent analogues inhibited tumor cell growth with IC(50) values in the 10-20 microM range.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NMR studies reveal an unexpected binding site for a redox inhibitor of AP endonuclease 1.Biochemistry. 2011 Dec 6;50(48):10540-9. doi: 10.1021/bi201071g. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 22032234 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of novel analogues of E3330 that block the redox signaling activity of the multifunctional AP endonuclease/redox signaling enzyme APE1/Ref-1.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Apr 15;14(8):1387-401. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3410. Epub 2011 Jan 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 20874257 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of nuclease and redox activity of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox effector factor 1 (APE1/Ref-1).Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 May 1;25(9):2531-2544. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.01.028. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28161249 Review.
-
The redox function of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 as key modulator in photodynamic therapy.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2020 Oct;211:111992. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2020.111992. Epub 2020 Aug 11. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2020. PMID: 32805556
-
The DNA base excision repair protein Ape1/Ref-1 as a therapeutic and chemopreventive target.Mol Aspects Med. 2007 Jun-Aug;28(3-4):375-95. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2007.04.005. Epub 2007 May 3. Mol Aspects Med. 2007. PMID: 17560642 Review.
Cited by
-
Bridging population pharmacokinetic and semimechanistic absorption modeling of APX3330.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024 Jan;13(1):106-117. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13061. Epub 2023 Oct 26. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37884051 Free PMC article.
-
APE1/Ref-1 role in redox signaling: translational applications of targeting the redox function of the DNA repair/redox protein APE1/Ref-1.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;5(1):36-53. doi: 10.2174/1874467211205010036. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22122463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Inflammatory Signaling in Tet2 Mutant Preleukemic Cells Mitigates Stress-Induced Abnormalities and Clonal Hematopoiesis.Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Dec 6;23(6):833-849.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.10.013. Cell Stem Cell. 2018. PMID: 30526882 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting APE1: Advancements in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Tumors.Protein Pept Lett. 2025;32(1):18-33. doi: 10.2174/0109298665338519241114103223. Protein Pept Lett. 2025. PMID: 39648425 Review.
-
Impact of the APE1 Redox Function Inhibitor E3330 in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Exposed to Cisplatin: Increased Cytotoxicity and Impairment of Cell Migration and Invasion.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jun 24;9(6):550. doi: 10.3390/antiox9060550. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32599967 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

