The role of kinin B1 and B2 receptors in the scratching behaviour induced by proteinase-activated receptor-2 agonists in mice
- PMID: 20067469
- PMCID: PMC2829214
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00571.x
The role of kinin B1 and B2 receptors in the scratching behaviour induced by proteinase-activated receptor-2 agonists in mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: Activation of the proteinase-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2) induces scratching behaviour in mice. Here, we have investigated the role of kinin B(1) and B(2) receptors in the pruritogenic response elicited by activators of PAR-2.
Experimental approach: Scratching was induced by an intradermal (i.d.) injection of trypsin or the selective PAR-2 activating peptide SLIGRL-NH(2) at the back of the mouse neck. The animals were observed for 40 min and their scratching response was quantified.
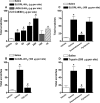
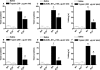
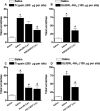
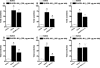
Key results: I.d. injection of trypsin or SLIGRL-NH(2) evoked a scratching behaviour, dependent on PAR-2 activation. Mice genetically deficient in kinin B(1) or B(2) receptors exhibited reduced scratching behaviour after i.d. injection of trypsin or SLIGRL-NH(2). Treatment (i.p.) with the non-peptide B(1) or B(2)receptor antagonists SSR240612 and FR173657, respectively, prevented the scratching behaviour caused by trypsin or SLIGRL-NH(2). Nonetheless, only treatment i.p. with the peptide B(2)receptor antagonist, Hoe 140, but not the B(1)receptor antagonist (DALBK), inhibited the pruritogenic response to trypsin. Hoe 140 was also effective against SLIGRL-NH(2)-induced scratching behaviour when injected by i.d. or intrathecal (i.t.) routes. Also, the response to SLIGRL-NH(2) was inhibited by i.t. (but not by i.d.) treatment with DALBK. Conversely, neither Hoe 140 nor DALBK were able to inhibit SLIGRL-NH(2)-induced scratching behaviour when given intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.).
Conclusions and implications: The present results demonstrated that kinins acting on both B(1) and B(2) receptors played a crucial role in controlling the pruriceptive signalling triggered by PAR-2 activation in mice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-nociceptive effect of kinin B₁ and B₂ receptor antagonists on peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2b):681-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01408.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21470206 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the role of neurogenic inflammation components in trypsin-elicited scratching behaviour in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Jul;154(5):1094-103. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.172. Epub 2008 May 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18454165 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the bradykinin 1 receptor antagonist SSR240612 after oral administration in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2018 Mar;109:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2018. PMID: 29559112
-
Kinins and their B1 and B2 receptors as potential therapeutic targets for pain relief.Life Sci. 2023 Feb 1;314:121302. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121302. Epub 2022 Dec 17. Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36535404 Review.
-
An overview of kinin mediated events in cancer progression and therapeutic applications.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022 Nov;1877(6):188807. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188807. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36167271 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms Underlying the Scratching Behavior Induced by the Activation of Proteinase-Activated Receptor-4 in Mice.J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Oct;135(10):2484-2491. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.183. Epub 2015 May 8. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25955385
-
Diversification of PAR signaling through receptor crosstalk.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Sep 10;27(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00382-0. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36088291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into the mechanisms of itch: are pain and itch controlled by distinct mechanisms?Pflugers Arch. 2013 Dec;465(12):1671-85. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1284-2. Epub 2013 May 1. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 23636773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ticks' tricks: immunomodulatory effects of ixodid tick saliva at the cutaneous tick-host interface.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 27;16:1520665. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1520665. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40213541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-nociceptive effect of kinin B₁ and B₂ receptor antagonists on peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2b):681-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01408.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21470206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyce S, Rupniak N, Carlson EJ, Webb J, Borkowski JA, Hess F, et al. Nociception and inflammatory hyperalgesia in B2 bradykinin receptor knockout mice. Immunopharmacology. 1996;33:333–335. - PubMed
-
- Calixto JB, Cabrini DA, Ferreira J, Campos MM. Kinins in pain and inflammation. Pain. 2000;87:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Calixto JB, Cabrini DA, Ferreira J, Campos MM. Inflamatory pain: kinins and antagonists. Cur Op Anesthesiol. 2001;14:519–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

