Rapid and reliable generation of invariant natural killer T-cell lines in vitro
- PMID: 20067532
- PMCID: PMC2770680
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03130.x
Rapid and reliable generation of invariant natural killer T-cell lines in vitro
Abstract
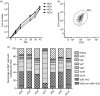
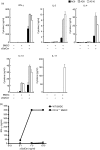
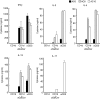
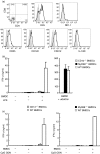
Several tools have proved useful in the study of invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells, including CD1d-deficient mice, J alpha281-deficient mice, synthetic lipid antigens and antigen-loaded CD1d tetramers. However, the generation and examination of long-term primary murine iNKT cell lines in vitro has been challenging. Here, we show the rapid generation of iNKT cell lines from splenic iNKT cells of V alpha14 T-cell receptor (TCR) transgenic (Tg) mice. These purified iNKT cells were stimulated by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) loaded with alpha-galactosylceramide (alphaGalCer) and cultured with interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-7. iNKT cells proliferated dramatically, and the cell number exhibited a 100-fold increase within 2 weeks and a 10(5)-fold increase in 8 weeks after repeated stimulation with alphaGalCer. The iNKT cell lines consisted of iNKT cells expressing V beta chains including V beta8.1/8.2, V beta14, V beta10, V beta6 and V beta7, and responded to stimulation with alphaGalCer presented both by BMDCs and by plate-bound CD1d. In addition, the iNKT cell lines produced interferon (IFN)-gamma when activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN)-stimulated BMDCs. Further, we show that iNKT cell lines produced cytokines in response to microbial antigens. In summary, high-yield iNKT cell lines were generated very rapidly and robustly expanded, and these iNKT cells responded to both TCR and cytokine stimulation in vitro. Given the desire to study primary iNKT cells for many purposes, these iNKT cell lines should provide an important tool for the study of iNKT cell subsets, antigen and TCR specificity, activation, inactivation and effector functions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The complementarity determining region 2 of BV8S2 (V beta 8.2) contributes to antigen recognition by rat invariant NKT cell TCR.J Immunol. 2006 Jun 15;176(12):7447-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.12.7447. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16751390
-
Plasticity of invariant NKT cell regulation of allergic airway disease is dependent on IFN-gamma production.J Immunol. 2010 Jul 1;185(1):253-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902301. Epub 2010 Jun 4. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20525882
-
Identification of distinct human invariant natural killer T-cell response phenotypes to alpha-galactosylceramide.BMC Immunol. 2008 Dec 3;9:71. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-9-71. BMC Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19055753 Free PMC article.
-
Turned on by danger: activation of CD1d-restricted invariant natural killer T cells.Immunology. 2012 Sep;137(1):20-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03612.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22734667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of CD1d-Restricted Invariant Natural Killer T Cells in Antimicrobial Immunity and Potential Applications for Infection Control.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 6;9:1266. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01266. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29928278 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Optimized Method for Isolating and Expanding Invariant Natural Killer T Cells from Mouse Spleen.J Vis Exp. 2015 Oct 29;(105):e53256. doi: 10.3791/53256. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 26555769 Free PMC article.
-
Next Generation Sequencing of the Pig αβ TCR Repertoire Identifies the Porcine Invariant NKT Cell Receptor.J Immunol. 2019 Apr 1;202(7):1981-1991. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801171. Epub 2019 Feb 18. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30777925 Free PMC article.
-
Innate recognition of cell wall β-glucans drives invariant natural killer T cell responses against fungi.Cell Host Microbe. 2011 Nov 17;10(5):437-50. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.09.011. Cell Host Microbe. 2011. PMID: 22100160 Free PMC article.
-
iNKT cell production of GM-CSF controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jan;10(1):e1003805. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003805. Epub 2014 Jan 2. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24391492 Free PMC article.
-
Enterogenous bacterial glycolipids are required for the generation of natural killer T cells mediated liver injury.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 8;6:36365. doi: 10.1038/srep36365. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27821872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brigl M, Brenner MB. CD1: antigen presentation and T cell function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:817–90. - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg M. Toward an understanding of NKT cell biology. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:877–900. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:297–336. - PubMed
-
- Mattner J, Debord KL, Ismail N, et al. Exogenous and endogenous glycolipid antigens activate NKT cells during microbial infections. Nature. 2005;434:525–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

