Characterization of a variant vlhA gene of Mycoplasma synoviae, strain WVU 1853, with a highly divergent haemagglutinin region
- PMID: 20067616
- PMCID: PMC2825196
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-6
Characterization of a variant vlhA gene of Mycoplasma synoviae, strain WVU 1853, with a highly divergent haemagglutinin region
Abstract
Background: In Mycoplasma synoviae, type strain WVU 1853, a single member of the haemaglutinin vlhA gene family has been previously shown to be expressed. Variants of vlhA are expressed from the same unique vlhA promoter by recruiting pseudogene sequences via site-specific recombination events, thus generating antigenic variability. Using a bacterial stock of M. synoviae WVU 1853 that had been colony purified thrice and maintained in our laboratory at low passage level, we previously identified a vlhA gene-related partial coding sequence, referred to as MS2/28.1. The E. coli-expressed product of this partial coding sequence was found to be immunodominant, suggesting that it might be expressed.
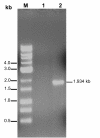
Results: Reverse transcription-PCR amplification (RT-PCR), using a sense primer located at the 5'-end region of the expected vlhA transcript and a reverse primer located at the 3' end of MS2/28.1 coding sequence, yielded a consistent amplification product showing that MS2/28.1 was indeed transcribed. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the RT-PCR product identified an 1815-nucleotide full-length open reading frame (ORF), immediately preceded by a nucleotide sequence identical to that previously reported for expressed vlhA genes. PCR amplifications using genomic DNA isolated from single colonies further confirmed that the full-length ORF of MS2/28.1 was located downstream of the unique vlhA promoter sequence. The deduced 604-amino acid (aa) sequence showed a perfect sequence identity to the previously reported vlhA expressed genes along the first 224 residues, then highly diverged with only 37.6% aa identity. Despite the fact that this M. synoviae clone expressed a highly divergent and considerably shorter C-terminal haemagglutinin product, it was found to be expressed at the surface of the bacterium and was able to haemagglutinate chicken erythrocytes. Importantly, the E. coli-expressed C-terminal highly divergent 60 residues of MS2/28.1 proved haemagglutination competent.
Conclusions: In contrast to the previously characterized vlhA expressed variants, MS2/28.1 displayed a highly divergent sequence, while still able to haemagglutinate erythrocytes. Overall, the data provide an indication as to which extent the M. synoviae vlhA gene could vary its antigenic repertoire.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characterization of the antigenic and functional domains of a Mycoplasma synoviae variant vlhA gene.Vet Microbiol. 2012 May 4;156(3-4):322-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.11.016. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Vet Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22176762
-
A novel mechanism for control of antigenic variation in the haemagglutinin gene family of mycoplasma synoviae.Mol Microbiol. 2000 Feb;35(4):911-23. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01766.x. Mol Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10692167
-
The vlhA loci of Mycoplasma synoviae are confined to a restricted region of the genome.Microbiology (Reading). 2005 Mar;151(Pt 3):935-940. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27109-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2005. PMID: 15758238
-
Development and evaluation of an improved diagnostic PCR for Mycoplasma synoviae using primers located in the haemagglutinin encoding gene vlhA and its value for strain typing.Vet Microbiol. 2009 Apr 14;136(1-2):61-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.10.011. Epub 2008 Nov 1. Vet Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19046834
-
Haemagglutinins of pathogenic avian mycoplasmas.Avian Pathol. 2002 Dec;31(6):535-47. doi: 10.1080/0307945021000024526. Avian Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12593736 Review.
Cited by
-
A sialoreceptor binding motif in the Mycoplasma synoviae adhesin VlhA.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 22;9(10):e110360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110360. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25338071 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothetical Proteins of Mycoplasma synoviae Reannotation and Expression Changes Identified via RNA-Sequencing.Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 6;11(11):2716. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112716. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004728 Free PMC article.
-
Mm19, a Mycoplasma meleagridis Major Surface Nuclease that Is Related to the RE_AlwI Superfamily of Endonucleases.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 24;11(3):e0152171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152171. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27010566 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomics of Mycoplasma synoviae and New Targets for Molecular Diagnostics.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Feb 19;8:640067. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.640067. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33681335 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of expressed vlhA adhesin sequences and intermediate hemagglutination phenotypes in Mycoplasma synoviae.J Bacteriol. 2011 May;193(9):2116-21. doi: 10.1128/JB.00022-11. Epub 2011 Mar 4. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21378196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kleven SH. In: Diseases of Poultry. Saif YM, Barnes HJ, Glisson JR, Fadly AR, McDougald LR, Swayne DE, editor. Iowa State Press Ames; 2003. Mycoplasma synoviae infection; p. 756.
-
- Vasconcelos AT, Ferreira HB, Bizarro CV, Bonatto SL, Carvalho MO, Pinto PM, Almeida DF, Almeida LG, Almeida R, Alves-Filho L, Assunção EN, Azevedo VA, Bogo MR, Brigido MM, Brocchi M, Burity HA, Camargo AA, Camargo SS, Carepo MS, Carraro DM, de Mattos Cascardo JC, Castro LA, Cavalcanti G, Chemale G, Collevatti RG, Cunha CW, Dallagiovanna B, Dambrós BP, Dellagostin OA, Falcão C, Fantinatti-Garboggini F, Felipe MS, Fiorentin L, Franco GR, Freitas NS, Frías D, Grangeiro TB, Grisard EC, Guimarães CT, Hungria M, Jardim SN, Krieger MA, Laurino JP, Lima LF, Lopes MI, Loreto EL, Madeira HM, Manfio GP, Maranhão AQ, Martinkovics CT, Medeiros SR, Moreira MA, Neiva M, Ramalho-Neto CE, Nicolás MF, Oliveira SC, Paixão RF, Pedrosa FO, Pena SD, Pereira M, Pereira-Ferrari L, Piffer I, Pinto LS, Potrich DP, Salim AC, Santos FR, Schmitt R, Schneider MP, Schrank A, Schrank IS, Schuck AF, Seuanez HN, Silva DW, Silva R, Silva SC, Soares CM, Souza KR, Souza RC, Staats CC, Steffens MB, Teixeira SM, Urmenyi TP, Vainstein MH, Zuccherato LW, Simpson AJ, Zaha A. Swine and Poultry Pathogens: the Complete Genome Sequences of Two Strains of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and a Strain of Mycoplasma synoviae. J Bacteriol. 2005;187:5568–5577. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.16.5568-5577.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sirand-Pugnet P, Lartigue C, Marenda M, Jacob D, Barré A, Barbe V, Schenowitz C, Mangenot S, Couloux A, Segurens B, de Daruvar A, Blanchard A, Citti C. Being pathogenic plastic, and sexual while living with a nearly minimal bacterial genome. PLoS Genet. 2007;3:744–758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030075. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

