Rac1 and Cdc42 are regulators of HRasV12-transformation and angiogenic factors in human fibroblasts
- PMID: 20067638
- PMCID: PMC2826294
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-13
Rac1 and Cdc42 are regulators of HRasV12-transformation and angiogenic factors in human fibroblasts
Abstract
Background: The activities of Rac1 and Cdc42 are essential for HRas-induced transformation of rodent fibroblasts. What is more, expression of constitutively activated mutants of Rac1 and/or Cdc42 is sufficient for their malignant transformation. The role for these two Rho GTPases in HRas-mediated transformation of human fibroblasts has not been studied. Here we evaluated the contribution of Rac1 and Cdc42 to maintaining HRas-induced transformation of human fibroblasts, and determined the ability of constitutively activated mutants of Rac1 or Cdc42 to induce malignant transformation of a human fibroblast cell strain.
Methods: Under the control of a tetracycline regulatable promoter, dominant negative mutants of Rac1 and Cdc42 were expressed in a human HRas-transformed, tumor derived fibroblast cell line. These cells were used to determine the roles of Rac1 and/or Cdc42 proteins in maintaining HRas-induced transformed phenotypes. Similarly, constitutively active mutants were expressed in a non-transformed human fibroblast cell strain to evaluate their potential to induce malignant transformation. Affymetrix GeneChip arrays were used for transcriptome analyses, and observed expression differences were subsequently validated using protein assays.
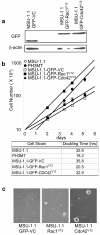
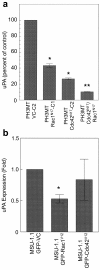
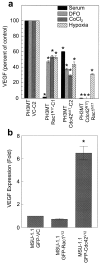
Results: Expression of dominant negative Rac1 and/or Cdc42 significantly altered transformed phenotypes of HRas malignantly transformed human fibroblasts. In contrast, expression of constitutively active mutants of Rac1 or Cdc42 was not sufficient to induce malignant transformation. Microarray analysis revealed that the expression of 29 genes was dependent on Rac1 and Cdc42, many of which are known to play a role in cancer. The dependence of two such genes, uPA and VEGF was further validated in both normoxic and hypoxic conditions.
Conclusion(s): The results presented here indicate that expression of both Rac1 and Cdc42 is necessary for maintaining several transformed phenotypes in oncogenic HRas transformed human cells, including their ability to form tumors in athymic mice. Our data also indicate that expression of either activated Rac1 or Cdc42 alone is not sufficient for malignant transformation of human fibroblasts, although each is required for specific transformed phenotypes. Furthermore, our study elucidates that the expression of several highly significant cancer related genes require the activities of Rac1 and/or Cdc42 which may also play a critical role in cellular transformation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Cdc42, and Rac1 act downstream of Ras in integrin-dependent neurite outgrowth in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jan;20(1):158-72. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.1.158-172.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10594018 Free PMC article.
-
Role of activated Rac1/Cdc42 in mediating endothelial cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis in breast cancer.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 4;8(6):e66275. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066275. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2020 Oct 8;15(10):e0240575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240575. PMID: 23750283 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Role of Rac1 and Cdc42 in hypoxia induced p53 and von Hippel-Lindau suppression and HIF1alpha activation.Int J Cancer. 2006 Jun 15;118(12):2965-72. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21763. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16395716
-
The role of Rho GTPases' substrates Rac and Cdc42 in osteoclastogenesis and relevant natural medicinal products study.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jul 31;40(7):BSR20200407. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200407. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32578854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Cdc42 and Rac1 activities in pheochromocytoma, the adrenal medulla tumor.Small GTPases. 2017 Apr 3;8(2):122-127. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1202634. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Small GTPases. 2017. PMID: 27355516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear expression of Rac1 in cervical premalignant lesions and cervical cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2012 Mar 23;12:116. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-116. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22443139 Free PMC article.
-
Systems-wide analysis of K-Ras, Cdc42, and PAK4 signaling by quantitative phosphoproteomics.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Aug;12(8):2070-80. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.027052. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23608596 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of Cdc42 in Ras-induced transformation revealed by gene targeting.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e37317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037317. Epub 2012 Jun 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22719838 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-Plasma Membrane Interaction in Live Cells and the Influence of GPI Glycan Structure on the Interaction.Chemistry. 2024 Feb 7;30(8):e202303047. doi: 10.1002/chem.202303047. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Chemistry. 2024. PMID: 37966101 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc42 in oncogenic transformation, invasion, and tumorigenesis.Cell Signal. 2011 Sep;23(9):1415-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.04.001. Epub 2011 Apr 16. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21515363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

