Identification of known drugs that act as inhibitors of NF-kappaB signaling and their mechanism of action
- PMID: 20067776
- PMCID: PMC2834878
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.12.021
Identification of known drugs that act as inhibitors of NF-kappaB signaling and their mechanism of action
Abstract
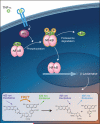
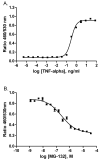
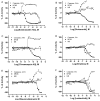
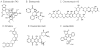
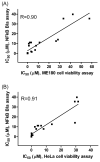
Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) is a transcription factor that plays a critical role across many cellular processes including embryonic and neuronal development, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and immune responses to infection and inflammation. Dysregulation of NF-kappaB signaling is associated with inflammatory diseases and certain cancers. Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB signaling has been found in some types of tumors including breast, colon, prostate, skin and lymphoid, hence therapeutic blockade of NF-kappaB signaling in cancer cells provides an attractive strategy for the development of anticancer drugs. To identify small molecule inhibitors of NF-kappaB signaling, we screened approximately 2800 clinically approved drugs and bioactive compounds from the NIH Chemical Genomics Center Pharmaceutical Collection (NPC) in a NF-kappaB mediated beta-lactamase reporter gene assay. Each compound was tested at fifteen different concentrations in a quantitative high throughput screening format. We identified nineteen drugs that inhibited NF-kappaB signaling, with potencies as low as 20 nM. Many of these drugs, including emetine, fluorosalan, sunitinib malate, bithionol, narasin, tribromsalan, and lestaurtinib, inhibited NF-kappaB signaling via inhibition of IkappaBalpha phosphorylation. Others, such as ectinascidin 743, chromomycin A3 and bortezomib utilized other mechanisms. Furthermore, many of these drugs induced caspase 3/7 activity and had an inhibitory effect on cervical cancer cell growth. Our results indicate that many currently approved pharmaceuticals have previously unappreciated effects on NF-kappaB signaling, which may contribute to anticancer therapeutic effects. Comprehensive profiling of approved drugs provides insight into their molecular mechanisms, thus providing a basis for drug repurposing.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel blocker of I kappa B alpha kinase that enhances cellular apoptosis and inhibits cellular invasion through suppression of NF-kappa B-regulated gene products.J Immunol. 2005 Jun 1;174(11):7383-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.11.7383. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15905586
-
Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid potentiates apoptosis, inhibits invasion, and abolishes osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NF-kappa B and NF-kappa B-regulated gene expression.J Immunol. 2006 Mar 1;176(5):3127-40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.5.3127. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16493072
-
Inhibition of the NEMO/IKKβ association complex formation, a novel mechanism associated with the NF-κB activation suppression by Withania somnifera's key metabolite withaferin A.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 2;11 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-S4-S25. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21143809 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB Signaling Pathway Inhibitors as Anticancer Drug Candidates.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(4):483-490. doi: 10.2174/1871520616666160729112854. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27481554 Review.
-
NF-kappaB as a potential molecular target for cancer therapy.Biofactors. 2007;29(1):19-35. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520290103. Biofactors. 2007. PMID: 17611291 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of death domain proteins in host response upon SARS-CoV-2 infection: modulation of programmed cell death and translational applications.Cell Death Discov. 2020 Oct 10;6(1):101. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-00331-w. eCollection 2020. Cell Death Discov. 2020. PMID: 33072409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of repurposed small molecule drugs for chordoma therapy.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Jul;14(7):638-47. doi: 10.4161/cbt.24596. Epub 2013 May 10. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23792643 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcococca saligna extract attenuates formaldehyde-induced arthritis in Wistar rats via modulation of pro-inflammatory and inflammatory biomarkers.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Apr;30(2):579-597. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-00929-9. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35218463
-
High-throughput Giardia lamblia viability assay using bioluminescent ATP content measurements.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Feb;55(2):667-75. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00618-10. Epub 2010 Nov 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21078930 Free PMC article.
-
CAF hierarchy driven by pancreatic cancer cell p53-status creates a pro-metastatic and chemoresistant environment via perlecan.Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 12;10(1):3637. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10968-6. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31406163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen F, Bower J, Demers JM, Shi X. Upstream Signal Transduction of NF-kB Activation. Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology. 2002;6:345–69.
-
- Gilmore TD. Introduction to NF-kappaB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene. 2006;25:6680–4. - PubMed
-
- Ahn KS, Aggarwal BB. Transcription factor NF-kappaB: a sensor for smoke and stress signals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1056:218–33. - PubMed
-
- Lee CH, Jeon YT, Kim SH, Song YS. NF-kappaB as a potential molecular target for cancer therapy. Biofactors. 2007;29:19–35. - PubMed
-
- Hacker H, Karin M. Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases. Sci STKE. 2006;2006:re13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

