Regional convection-enhanced delivery of gadolinium-labeled albumin in the rat hippocampus in vivo
- PMID: 20067808
- PMCID: PMC2938958
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.01.002
Regional convection-enhanced delivery of gadolinium-labeled albumin in the rat hippocampus in vivo
Abstract
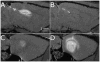
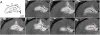
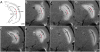
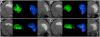
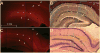
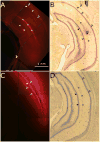
Convection-enhanced delivery (CED) has emerged as a promising method of targeted drug delivery for treating central nervous system (CNS) disorders, but the influence of brain structure on infusate distribution is unclear. We have utilized this approach to study extracellular transport and distribution of a contrast agent in the hippocampus, a complex structure susceptible to CNS disorders. The magnetic resonance (MR) contrast agent diethylene triamene penta-acetic acid chelated gadolinium-labeled albumin (Gd-albumin), tagged with Evans blue dye, was directly infused (V(i)=5 microl) into the dorsal and ventral hippocampus of seven male Sprague-Dawley rats. The final distribution profile of the contrast agent, a product of CED and limited diffusion, was observed in vivo using high-resolution T1-weighted MR imaging at 11.1T. Dense cell layers, such as the granule cell layer of the dentate gyrus and the pyramidal cell layer of CA1, appeared to be barriers to transport of the tracer. Three-dimensional distribution shape and volume (V(d)) differences, between the dorsal and ventral hippocampus infusions, were determined from the MR images using a semi-automatic segmentation routine (dorsal V(d)=23.4+/-1.8 microl, ventral V(d)=36.4+/-5.1 microl). Finer structural detail of the hippocampus was obtained using a combination of histological analysis and fluorescence imaging. This study demonstrates that CED has the potential to target all regions of the hippocampus and that tracer distribution is influenced by infusion site, underlying structure and circuitry, and extent of backflow. Therefore, CED, combined with high-resolution MR imaging, may be a useful strategy for delivering therapeutics for the treatment of CNS disorders affecting the hippocampus.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Voxelized computational model for convection-enhanced delivery in the rat ventral hippocampus: comparison with in vivo MR experimental studies.Ann Biomed Eng. 2012 Sep;40(9):2043-58. doi: 10.1007/s10439-012-0566-8. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Ann Biomed Eng. 2012. PMID: 22532321 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of Gd-albumin delivery to the rat hippocampus in vivo by convection-enhanced delivery.J Neurosci Methods. 2012 Jul 30;209(1):62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.05.024. Epub 2012 Jun 8. J Neurosci Methods. 2012. PMID: 22687936 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of neuropathology on convection-enhanced delivery in the rat hippocampus.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 8;8(11):e80606. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080606. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260433 Free PMC article.
-
Albumin labeled with Gd-DTPA. An intravascular contrast-enhancing agent for magnetic resonance blood pool and perfusion imaging.Acta Radiol Suppl. 1990;374:99-102. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1990. PMID: 1966977 Review.
-
Imaging of Convective Drug Delivery in the Nervous System.Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2017 Oct;28(4):615-622. doi: 10.1016/j.nec.2017.05.012. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2017. PMID: 28917289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Voxelized computational model for convection-enhanced delivery in the rat ventral hippocampus: comparison with in vivo MR experimental studies.Ann Biomed Eng. 2012 Sep;40(9):2043-58. doi: 10.1007/s10439-012-0566-8. Epub 2012 Apr 25. Ann Biomed Eng. 2012. PMID: 22532321 Free PMC article.
-
The MRI contrast agent gadoteridol enhances distribution of rAAV1 in the rat hippocampus.Gene Ther. 2013 Dec;20(12):1172-7. doi: 10.1038/gt.2013.47. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Gene Ther. 2013. PMID: 24048419 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-carrying microbubbles as a theranostic tool in convection-enhanced delivery for brain tumor therapy.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 27;8(26):42359-42371. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16218. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28418846 Free PMC article.
-
Time-reversal acoustics and ultrasound-assisted convection-enhanced drug delivery to the brain.J Acoust Soc Am. 2013 Aug;134(2):1569-75. doi: 10.1121/1.4812879. J Acoust Soc Am. 2013. PMID: 23927197 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Delivery to the Brain: Recent Advances and Unmet Challenges.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 23;15(12):2658. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122658. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38139999 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abujudeh HH, Kaewlai R, Kagan A, Chibnik LB, Nazarian RM, High WA, Kay J. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis after gadopentetate dimeglumine exposure: case series of 36 patients. Radiology. 2009;253:81–9. - PubMed
-
- Andersen AH. On the Rician distribution of noisy MRI data. Magn Reson Med. 1996;36:331–3. - PubMed
-
- Andersen P, Bliss TV, Lomo T, Olsen LI, Skrede KK. Lamellar organization of hippocampal excitatory pathways. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969;76:4A–5A. - PubMed
-
- Auer RN, Siesjo BK. Biological differences between ischemia, hypoglycemia, and epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1988;24:699–707. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

