Nlrc4/Ipaf/CLAN/CARD12: more than a flagellin sensor
- PMID: 20067841
- PMCID: PMC2862870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.01.003
Nlrc4/Ipaf/CLAN/CARD12: more than a flagellin sensor
Abstract
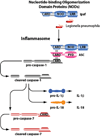
Nlrc4 is a member of the Nod-like receptors (NLRs), a family of cytosolic receptors involved in sensing bacterial molecules. NLRs are a group of proteins containing spans of leucine-rich repeats that senses bacterial factors within the eukaryotic cytosol. The recognition of bacterial factors provokes the formation of the inflammasome complex which includes specific NLRs. The inflammasome is responsible for caspase-1 activation which leads to the cleavage and maturation of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1beta and IL-18. Nlrc4 was considered to be a devoted flagellin sensor in eukaryotic cells. However, studies using a variety of pathogens such as Salmonella, Legionella, Shigella and Pseudomonas at high bacterial burdens revealed that Nlrc4 can mediate caspase-1 activation independent of bacterial flagellin. On the other hand, new reports showed that Nlrc4 can restrict bacterial infection independently of caspase-1. Therefore, Nlrc4 maybe involved in sensing more than one bacterial molecule and may participate in several immune complexes.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Amer A, Franchi L, Kanneganti TD, Body-Malapel M, Ozoren N, Brady G, et al. Regulation of Legionella phagosome maturation and infection through flagellin and host Ipaf. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:35217–35223. - PubMed
-
- Amer AO. Modulation of caspases and their non-apoptotic functions by Legionella pneumophila. Cell. Microbiol. 2009 Epub ahead of print. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

