Effects of resveratrol on proliferation and apoptosis in rat ovarian theca-interstitial cells
- PMID: 20067985
- PMCID: PMC2834407
- DOI: 10.1093/molehr/gaq002
Effects of resveratrol on proliferation and apoptosis in rat ovarian theca-interstitial cells
Abstract
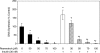
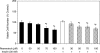
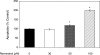
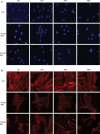
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is characterized by ovarian dysfunction and associated with ovarian theca-interstitial (T-I) cell hyperplasia, hyperinsulinemia, systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. This in vitro study tested whether rat T-I cell growth with or without insulin can be altered by resveratrol, a natural polyphenol with anti-carcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and antioxidant properties. Rat T-I cells were cultured with and without resveratrol and/or insulin, and the effects on DNA synthesis, number of viable cells and markers of apoptosis were evaluated. Resveratrol alone induced a potent concentration-dependent inhibition of cell growth by inhibiting DNA synthesis, decreasing the number of viable cells and increasing the activity of executioner caspases 3 and 7; these effects of resveratrol counteracted the pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic effects of insulin. Immunofluorescence analysis of cells incubated with resveratrol showed concentration- and time-dependent morphological changes consistent with apoptosis. The present findings indicate that resveratrol promotes apoptosis to reduce rat T-I cell growth in vitro as well as inhibiting insulin-induced rat T-I cell growth. This suggests a possibility that resveratrol and/or mechanisms mediating its effect may be relevant to the development of novel treatments for PCOS, which is characterized by both excessive ovarian mesenchyma growth and hyperinsulinemia.
Figures
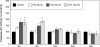
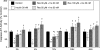
Similar articles
-
Resveratrol potentiates effects of simvastatin on inhibition of rat ovarian theca-interstitial cells steroidogenesis.J Ovarian Res. 2014 Feb 13;7:21. doi: 10.1186/1757-2215-7-21. J Ovarian Res. 2014. PMID: 24524197 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol reduces steroidogenesis in rat ovarian theca-interstitial cells: the role of inhibition of Akt/PKB signaling pathway.Endocrinology. 2012 Aug;153(8):4019-29. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1385. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22719052 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol inhibits the mevalonate pathway and potentiates the antiproliferative effects of simvastatin in rat theca-interstitial cells.Fertil Steril. 2011 Nov;96(5):1252-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.08.010. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Fertil Steril. 2011. PMID: 21907337
-
Ovarian actions of resveratrol.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 Aug;1348(1):86-96. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12875. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 26315293 Review.
-
Molecular mechanism of the chemopreventive effect of resveratrol.Mutat Res. 2003 Feb-Mar;523-524:145-50. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(02)00330-5. Mutat Res. 2003. PMID: 12628512 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanocomposites based on nanoceria regulate the immune microenvironment for the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Nov 7;21(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02182-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37936120 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol potentiates effects of simvastatin on inhibition of rat ovarian theca-interstitial cells steroidogenesis.J Ovarian Res. 2014 Feb 13;7:21. doi: 10.1186/1757-2215-7-21. J Ovarian Res. 2014. PMID: 24524197 Free PMC article.
-
Mediterranean Diet Nutrients to Turn the Tide against Insulin Resistance and Related Diseases.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 12;12(4):1066. doi: 10.3390/nu12041066. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32290535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol promotes expression of SIRT1 and StAR in rat ovarian granulosa cells: an implicative role of SIRT1 in the ovary.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2012 Feb 23;10:14. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-10-14. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22357324 Free PMC article.
-
Mediterranean Diet as an Antioxidant: The Impact on Metabolic Health and Overall Wellbeing.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 6;13(6):1951. doi: 10.3390/nu13061951. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34204057 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alkhalaf M, El-Mowafy A, Renno W, Rachid O, Ali A, Al-Attyiah R. Resveratrol-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells is mediated primarily through the caspase-3-dependent pathway. Arch Med Res. 2008;39:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Atencia R, Asumendi A, Garcia-Sanz M. Role of cytoskeleton in apoptosis. Vitam Horm. 2000;58:267–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

