The TRC8 ubiquitin ligase is sterol regulated and interacts with lipid and protein biosynthetic pathways
- PMID: 20068067
- PMCID: PMC3086825
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0491
The TRC8 ubiquitin ligase is sterol regulated and interacts with lipid and protein biosynthetic pathways
Abstract
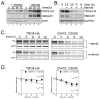
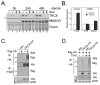
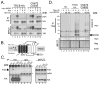
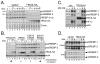
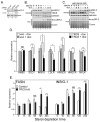
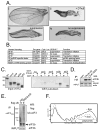
TRC8/RNF139 encodes an endoplasmic reticulum-resident E3 ubiquitin ligase that inhibits growth in a RING- and ubiquitylation-dependent manner. TRC8 also contains a predicted sterol-sensing domain. Here, we report that TRC8 protein levels are sterol responsive and that it binds and stimulates ubiquitylation of the endoplasmic reticulum anchor protein INSIG. Induction of TRC8 destabilized the precursor forms of the transcription factors SREBP-1 and SREBP-2. Loss of SREBP precursors was proteasome dependent, required a functional RING domain, occurred without generating processed nuclear forms, and suppressed SREBP target genes. TRC8 knockdown had opposite effects in sterol-deprived cells. In Drosophila, growth inhibition by DTrc8 was genetically suppressed by loss of specific Mprlp, Padlp N-terminal domain-containing proteins found in the COP9 signalosome and eIF3. DTrc8 genetically and physically interacted with two eIF3 subunits: eIF3f and eIF3h. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments confirmed these interactions in mammalian cells, and TRC8 overexpression suppressed polysome profiles. Moreover, high-molecular weight ubiquitylated proteins were observed in eIF3 immunoprecipitations from TRC8-overexpressing cells. Thus, TRC8 function may provide a regulatory link between the lipid and protein biosynthetic pathways.
Figures
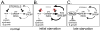
Similar articles
-
The sterol-sensing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane protein TRC8 hampers ER to Golgi transport of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 (SREBP-2)/SREBP cleavage-activated protein and reduces SREBP-2 cleavage.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 16;284(42):28995-9004. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.041376. Epub 2009 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19706601 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol-induced degradation of HMG CoA reductase depends on interplay of two Insigs and two ubiquitin ligases, gp78 and Trc8.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 20;108(51):20503-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112831108. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22143767 Free PMC article.
-
Ring finger protein 145 (RNF145) is a ubiquitin ligase for sterol-induced degradation of HMG-CoA reductase.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 16;293(11):4047-4055. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001260. Epub 2018 Jan 26. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29374057 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the ERAD ubiquitin E3 ligases for viral and cellular targeting of MHC class I.Mol Immunol. 2015 Dec;68(2 Pt A):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26210183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of lipid metabolism by regulated intramembrane proteolysis of sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs).Biochem Soc Symp. 2003;(70):221-31. doi: 10.1042/bss0700221. Biochem Soc Symp. 2003. PMID: 14587295 Review.
Cited by
-
A palindrome-mediated recurrent translocation with 3:1 meiotic nondisjunction: the t(8;22)(q24.13;q11.21).Am J Hum Genet. 2010 Aug 13;87(2):209-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.07.002. Epub 2010 Jul 30. Am J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20673865 Free PMC article.
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH6 degrades squalene monooxygenase and affects 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase and the cholesterol synthesis pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Apr;34(7):1262-70. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01140-13. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24449766 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes regulate human cytomegalovirus US2-mediated immunoreceptor downregulation.J Cell Sci. 2017 Sep 1;130(17):2883-2892. doi: 10.1242/jcs.206839. Epub 2017 Jul 25. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28743740 Free PMC article.
-
Friend or foe? Reciprocal regulation between E3 ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Feb 28;52(1):241-267. doi: 10.1042/BST20230454. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38414432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The translational factor eIF3f: the ambivalent eIF3 subunit.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Oct;70(19):3603-16. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1263-y. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23354061 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56(2):106–30. - PubMed
-
- Kaelin WG., Jr The von Hippel-Lindau protein, HIF hydroxylation, and oxygen sensing. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2005;338(1):627–38. - PubMed
-
- Mandriota SJ, Turner KJ, Davies DR, et al. HIF activation identifies early lesions in VHL kidneys: evidence for site-specific tumor suppressor function in the nephron. Cancer cell. 2002;1(5):459–68. - PubMed
-
- Tomlinson IP, Alam NA, Rowan AJ, et al. Germline mutations in FH predispose to dominantly inherited uterine fibroids, skin leiomyomata and papillary renal cell cancer. Nature genetics. 2002;30(4):406–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

