A phase I study of 7-t-butyldimethylsilyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin in adult patients with refractory or metastatic solid malignancies
- PMID: 20068096
- PMCID: PMC2831464
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2429
A phase I study of 7-t-butyldimethylsilyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin in adult patients with refractory or metastatic solid malignancies
Abstract
Purpose: 7-t-Butyldimethylsilyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (AR-67) is a novel third generation camptothecin selected for development based on the blood stability of its pharmacologically active lactone form and its high potency in preclinical models. Here, we report the initial phase I experience with i.v. AR-67 in adults with refractory solid tumors. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN AND METHODS: AR-67 was infused over 1 hour daily five times, every 21 days, using an accelerated titration trial design. Plasma was collected on the 1st and 4th day of cycle 1 to determine pharmacokinetic parameters.
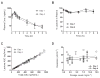
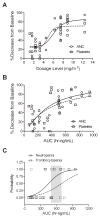
Results: Twenty-six patients were treated at nine dosage levels (1.2-12.4 mg/m(2)/d). Dose-limiting toxicities were observed in five patients and consisted of grade 4 febrile neutropenia, grade 3 fatigue, and grade 4 thrombocytopenia. Common toxicities included leukopenia (23%), thrombocytopenia (15.4%), fatigue (15.4%), neutropenia (11.5%), and anemia (11.5%). No diarrhea was observed. The maximum tolerated dosage was 7.5 mg/m(2)/d. The lactone form was the predominant species in plasma (>87% of area under the plasma concentration-time curve) at all dosages. No drug accumulation was observed on day 4. Clearance was constant with increasing dosage and hematologic toxicities correlated with exposure (P < 0.001). A prolonged partial response was observed in one subject with non-small cell lung cancer. Stable disease was noted in patients with small cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and duodenal cancer.
Conclusions: AR-67 is a novel, blood-stable camptothecin with a predictable toxicity profile and linear pharmacokinetics. The recommended phase II dosage is 7.5 mg/m(2)/d five times every 21 days.
Figures
References
-
- Hsiang YH, Hertzberg R, Hecht S, Liu LF. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:14873–8. - PubMed
-
- Hsiang YH, Liu LF. Identification of mammalian DNA topoisomerase I as an intracellular target of the anticancer drug camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1988;48:1722–6. - PubMed
-
- Hertzberg RP, Caranfa MJ, Holden KG, et al. Modification of the hydroxy lactone ring of camptothecin: inhibition of mammalian topoisomerase I and biological activity. J Med Chem. 1989;32:715–20. - PubMed
-
- Ziomkowska B, Cyrankiewicz M, Kruszewski S. Determination of hydroxycamptothecin affinities to albumin and membranes by steady-state fluorescence anisotropy measurements. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2007;10:486–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

