High glucose-induced oxidative stress increases transient receptor potential channel expression in human monocytes
- PMID: 20068131
- PMCID: PMC2844832
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-1100
High glucose-induced oxidative stress increases transient receptor potential channel expression in human monocytes
Abstract
Objective: Transient receptor potential (TRP) channel-induced cation influx activates human monocytes, which play an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. In the present study, we investigated the effects of high glucose-induced oxidative stress on TRP channel expression in human monocytes.
Research design and methods: Human monocytes were exposed to control conditions (5.6 mmol/l d-glucose), high glucose (30 mmol/l d-glucose or l-glucose), 100 micromol/l peroxynitrite, or high glucose in the presence of the superoxide dismutase mimetic tempol (100 micromol/l). TRP mRNA and TRP protein expression was measured using quantitative real-time RT-PCR and quantitative in-cell Western assay, respectively. Calcium influx and intracellular reactive oxygen species were measured using fluorescent dyes.
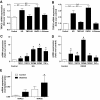
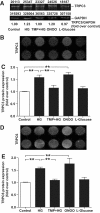
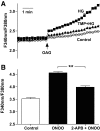
Results: Administration of high d-glucose significantly increased reactive oxygen species. High d-glucose or peroxynitrite significantly increased the expression of TRP canonical type 1 (TRPC1), TRPC3, TRPC5, TRPC6, TRP melastatin type 6 (TRPM6), and TRPM7 mRNA and TRPC3 and TRPC6 proteins. High d-glucose plus tempol or high l-glucose did not affect TRP expression. Increased oxidative stress by lipopolysaccharide or tumor necrosis factor-alpha increased TRP mRNA expression, whereas the reduction of superoxide radicals using diphenylene iodonium significantly reduced TRP mRNA expression. Increased TRPC3 and TRPC6 protein expression was accompanied by increased 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol-induced calcium influx, which was blocked by the TRPC inhibitor 2-aminoethoxydiphenylborane. TRPC6 mRNA was significantly higher in monocytes from 18 patients with type 2 diabetes compared with 28 control subjects (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: High d-glucose-induced oxidative stress increases TRP expression and calcium influx in human monocytes, pointing to a novel pathway for increased activation of monocytes and hence atherosclerosis in patients with diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Khaw KT, Wareham N, Bingham S, Luben R, Welch A, Day N: Association of hemoglobin A1c with cardiovascular disease and mortality in adults: the European prospective investigation into cancer in Norfolk. Ann Intern Med 2004; 141: 413– 420 - PubMed
-
- Ceriello A: Postprandial hyperglycemia and diabetes complications: is it time to treat? Diabetes 2005; 54: 1– 7 - PubMed
-
- Ross R: Atherosclerosis: an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: 115– 126 - PubMed
-
- Geissmann F, Jung S, Littman DR: Blood monocytes consist of two principal subsets with distinct migratory properties. Immunity 2003; 19: 71– 82 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

