Cannabinoid receptor 1 blockade ameliorates albuminuria in experimental diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 20068137
- PMCID: PMC2844813
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-1336
Cannabinoid receptor 1 blockade ameliorates albuminuria in experimental diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
Objective: Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) is localized in the central nervous system and in peripheral tissues involved in energy metabolism control. However, CB1 receptors are also expressed at low level within the glomeruli, and the aim of this study was to investigate their potential relevance in the pathogenesis of proteinuria in experimental type 1 diabetes.
Research design and methods: Streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice were treated with N-(piperidin-1-yl)-5-(4-iodophenyl)-1-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide (AM251), a selective CB1-receptor antagonist, at the dosage of 1 mg x kg(-1) x day(-1) via intraperitoneal injection for 14 weeks. Urinary albumin excretion was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. CB1 receptor expression was studied by immunohistochemistry, immunoblotting, and real-time PCR. Expression of nephrin, podocin, synaptopodin, and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) was assessed by immunofluorescence and real-time PCR. Fibronectin, transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1), and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) mRNA levels were quantitated by real-time PCR.
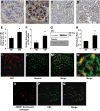
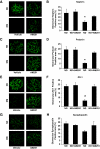
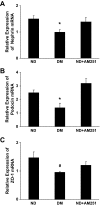
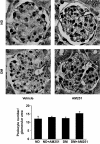
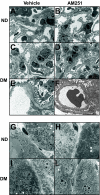
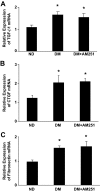
Results: In diabetic mice, the CB1 receptor was overexpressed within the glomeruli, predominantly by glomerular podocytes. Blockade of the CB1 receptor did not affect body weight, blood glucose, and blood pressure levels in either diabetic or control mice. Albuminuria was increased in diabetic mice compared with control animals and was significantly ameliorated by treatment with AM251. Furthermore, CB1 blockade completely prevented diabetes-induced downregulation of nephrin, podocin, and ZO-1. By contrast overexpression of fibronectin, TGF-beta1, and CTGF in renal cortex of diabetic mice was unaltered by AM251 administration.
Conclusions: In experimental type 1 diabetes, the CB1 receptor is overexpressed by glomerular podocytes, and blockade of the CB1 receptor ameliorates albuminuria possibly via prevention of nephrin, podocin, and ZO-1 loss.
Figures
References
-
- Molitch ME, DeFronzo RA, Franz MJ, Keane WF, Mogensen CE, Parving HH, Steffes MW: American Diabetes Association Nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: S79– S83 - PubMed
-
- Li JJ, Kwak SJ, Jung DS, Kim JJ, Yoo TH, Ryu DR, Han SH, Choi HY, Lee JE, Moon SJ, Kim DK, Han DS, Kang SW: Podocyte biology in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 2007; 106: S36– S42 - PubMed
-
- Wolf G, Chen S, Ziyadeh FN: From the periphery of the glomerular capillary wall toward the center of disease: podocyte injury comes of age in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2005; 54: 1626– 1634 - PubMed
-
- Pavenstädt H, Kriz W, Kretzler M: Cell biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol Rev 2003; 83: 253– 307 - PubMed
-
- Kestila M, Lenkkeri U, Mannikko M, Lamerdin J, McCready P, Putaala H, Ruotsalainen V, Morita T, Nissinen M, Herva R, Kashtan CE, Peltonen L, Holmberg C, Olsen A, Tryggvason K: Positionally cloned gene for a novel glomerular protein—nephrin—is mutated in congenital nephrotic syndrome. Mol Cell 1998; 1: 572– 578 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

