Inhibition of monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells and attenuation of atherosclerotic lesion by a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, exendin-4
- PMID: 20068138
- PMCID: PMC2844811
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-1694
Inhibition of monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells and attenuation of atherosclerotic lesion by a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, exendin-4
Abstract
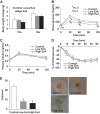
Objective: Exogenous administration of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) or GLP-1 receptor agonists such as an exendin-4 has direct beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system. However, their effects on atherosclerogenesis have not been elucidated. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of GLP-1 on accumulation of monocytes/macrophages on the vascular wall, one of the earliest steps in atherosclerogenesis.
Research design and methods: After continuous infusion of low (300 pmol . kg(-1) . day(-1)) or high (24 nmol . kg(-1) . day(-1)) dose of exendin-4 in C57BL/6 or apolipoprotein E-deficient mice (apoE(-/-)), we evaluated monocyte adhesion to the endothelia of thoracic aorta and arteriosclerotic lesions around the aortic valve. The effects of exendin-4 were investigated in mouse macrophages and human monocytes.
Results: Treatment with exendin-4 significantly inhibited monocytic adhesion in the aortas of C57BL/6 mice without affecting metabolic parameters. In apoE(-/-) mice, the same treatment reduced monocyte adhesion to the endothelium and suppressed atherosclerogenesis. In vitro treatment of mouse macrophages with exendin-4 suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced mRNA expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and suppressed nuclear translocation of p65, a component of nuclear factor-kappaB. This effect was reversed by either MDL-12330A, a cAMP inhibitor or PKI(14-22), a protein kinase A-specific inhibitor. In human monocytes, exendin-4 reduced the expression of CD11b.
Conclusions: Our data suggested that GLP-1 receptor agonists reduced monocyte/macrophage accumulation in the arterial wall by inhibiting the inflammatory response in macrophages, and that this effect may contribute to the attenuation of atherosclerotic lesion by exendin-4.
Figures




References
-
- Greig NH, Holloway HW, De Ore KA, Jani D, Wang Y, Zhou J, Garant MJ, Egan JM: Once daily injection of exendin-4 to diabetic mice achieves long-term beneficial effects on blood glucose concentrations. Diabetologia 1999; 42: 45– 50 - PubMed
-
- Kolterman OG, Buse JB, Fineman MS, Gaines E, Heintz S, Bicsak TA, Taylor K, Kim D, Aisporna M, Wang Y, Baron AD: Synthetic exendin-4 (exenatide) significantly reduces postprandial and fasting plasma glucose in subjects with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 3082– 3089 - PubMed
-
- Parkes DG, Pittner R, Jodka C, Smith P, Young A: Insulinotropic actions of exendin-4 and glucagon-like peptide-1 in vivo and in vitro. Metabolism 2001; 50: 583– 589 - PubMed
-
- Dupré J, Behme MT, McDonald TJ: Exendin-4 normalized postcibal glycemic excursions in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 3469– 3473 - PubMed
-
- Szayna M, Doyle ME, Betkey JA, Holloway HW, Spencer RG, Greig NH, Egan JM: Exendin-4 decelerates food intake, weight gain, and fat deposition in Zucker rats. Endocrinology 2000; 141: 1936– 1941 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

