Transcriptional autoregulation by BRCA1
- PMID: 20068145
- PMCID: PMC2952428
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1477
Transcriptional autoregulation by BRCA1
Abstract
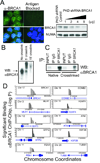
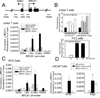
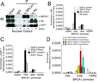
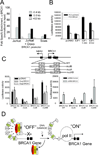
The BRCA1 gene product plays numerous roles in regulating genome integrity. Its role in assembling supermolecular complexes in response to DNA damage has been extensively studied; however, much less is understood about its role as a transcriptional coregulator. Loss or mutation is associated with hereditary breast and ovarian cancers, whereas altered expression occurs frequently in sporadic forms of breast cancer, suggesting that the control of BRCA1 transcription might be important to tumorigenesis. Here, we provide evidence of a striking linkage between the roles for BRCA1 as a transcriptional coregulator with control of its expression via an autoregulatory transcriptional loop. BRCA1 assembles with complexes containing E2F-1 and RB to form a repressive multicomponent transcriptional complex that inhibits BRCA1 promoter transcription. This complex is disrupted by genotoxic stress, resulting in the displacement of BRCA1 protein from the BRCA1 promoter and subsequent upregulation of BRCA1 transcription. Cells depleted of BRCA1 respond by upregulating BRCA1 transcripts, whereas cells overexpressing BRCA1 respond by downregulating BRCA1 transcripts. Tandem chromatin immmunoprecipitation studies show that BRCA1 is regulated by a dynamic coregulatory complex containing BRCA1, E2F1, and Rb at the BRCA1 promoter that is disrupted by DNA-damaging agents to increase its transcription. These results define a novel transcriptional mechanism of autoregulated homeostasis of BRCA1 that selectively titrates its levels to maintain genome integrity in response to genotoxic insult.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of BRCA1 expression by the Rb-E2F pathway.J Biol Chem. 2000 Feb 11;275(6):4532-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.6.4532. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10660629
-
c-Myc activates BRCA1 gene expression through distal promoter elements in breast cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2011 Jun 13;11:246. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-246. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21668996 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic coregulatory complex containing BRCA1, E2F1 and CtIP controls ATM transcription.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;30(3):596-608. doi: 10.1159/000341441. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22832221 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA1 gene in breast cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2003 Jul;196(1):19-41. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10257. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12767038 Review.
-
The role of the breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1) in sporadic epithelial ovarian cancer.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2003 Oct 7;1:72. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-1-72. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 14613551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ELL facilitates RNA polymerase II pause site entry and release.Nat Commun. 2012 Jan 17;3:633. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1652. Nat Commun. 2012. PMID: 22252557 Free PMC article.
-
ZC3H18 specifically binds and activates the BRCA1 promoter to facilitate homologous recombination in ovarian cancer.Nat Commun. 2019 Oct 11;10(1):4632. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12610-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31604914 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Analyses of Rare Germline Missense BRCA1 Variants Located within and outside Protein Domains with Known Functions.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;14(2):262. doi: 10.3390/genes14020262. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833189 Free PMC article.
-
The breast cancer susceptibility genes (BRCA) in breast and ovarian cancers.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014 Jan 1;19(4):605-18. doi: 10.2741/4230. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014. PMID: 24389207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A transcription-independent mechanism determines rapid periodic fluctuations of BRCA1 expression.EMBO J. 2023 Aug 1;42(15):e111951. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022111951. Epub 2023 Jun 19. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37334492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miki Y, Swensen J, Shattuck-Eidens D, et al. A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science. 1994;266:66–71. - PubMed
-
- Shen SX, Weaver Z, Xu X, et al. A targeted disruption of the murine Brca1 gene causes gamma-irradiation hypersensitivity and genetic instability. Oncogene. 1998;17:3115–3124. - PubMed
-
- Rosen EM, Fan S, Ma Y. BRCA1 regulation of transcription. Cancer Lett. 2006;236:175–185. - PubMed
-
- Mullan PB, Quinn JE, Harkin DP. The role of BRCA1 in transcriptional regulation and cell cycle control. Oncogene. 2006;25:5854–5863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

