Integrated protein array screening and high throughput validation of 70 novel neural calmodulin-binding proteins
- PMID: 20068228
- PMCID: PMC2877974
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M900324-MCP200
Integrated protein array screening and high throughput validation of 70 novel neural calmodulin-binding proteins
Abstract
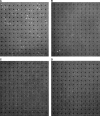
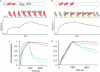
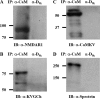
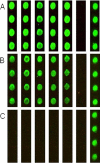
Calmodulin is an essential regulator of intracellular processes in response to extracellular stimuli mediated by a rise in Ca(2+) ion concentration. To profile protein-protein interactions of calmodulin in human brain, we probed a high content human protein array with fluorophore-labeled calmodulin in the presence of Ca(2+). This protein array contains 37,200 redundant proteins, incorporating over 10,000 unique human neural proteins from a human brain cDNA library. We designed a screen to find high affinity (K(D) < or = 1 microm) binding partners of calmodulin and identified 76 human proteins from all intracellular compartments of which 72 are novel. We measured the binding kinetics of 74 targets with calmodulin using a high throughput surface plasmon resonance assay. Most of the novel calmodulin-target complexes identified have low dissociation rates (k(off) < or = 10(-3) s(-1)) and high affinity (K(D) </= 1 mum), consistent with the design of the screen. Many of the identified proteins are known to assemble in neural tissue, forming assemblies such as the spectrin scaffold and the postsynaptic density. We developed a microarray of the identified target proteins with which we can characterize the biochemistry of calmodulin for all targets in parallel. Four novel targets were verified in neural cells by co-immunoprecipitation, and four were selected for exploration of the calmodulin-binding regions. Using synthetic peptides and isothermal titration calorimetry, calmodulin binding motifs were identified in the potassium voltage-gated channel Kv6.1 (residues 474-493), calmodulin kinase-like vesicle-associated protein (residues 302-316), EF-hand domain family member A2 (residues 202-216), and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type I, gamma (residues 400-415).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Probing calmodulin protein-protein interactions using high-content protein arrays.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;785:289-303. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-286-1_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21901608
-
High-throughput screening in two dimensions: binding intensity and off-rate on a peptide microarray.Anal Biochem. 2010 Jul 1;402(1):93-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2010.03.002. Epub 2010 Mar 6. Anal Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20211590
-
Identification and characterization of wolframin, the product of the wolfram syndrome gene (WFS1), as a novel calmodulin-binding protein.Biochemistry. 2009 May 12;48(18):3946-55. doi: 10.1021/bi900260y. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19292454
-
Structural Aspects and Prediction of Calmodulin-Binding Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 30;22(1):308. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010308. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33396740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calmodulin-binding domains in Alzheimer's disease proteins: extending the calcium hypothesis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Aug 6;320(4):1051-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.06.070. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15249195 Review.
Cited by
-
Ca2+ Signaling and Src Functions in Tumor Cells.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 3;13(12):1739. doi: 10.3390/biom13121739. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential Functions of Calmodulin and Identification of Its Proximal Interacting Proteins in Tachyzoite-Stage Toxoplasma gondii via BioID Technology.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0136322. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01363-22. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36214684 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin transduces Ca2+ oscillations into differential regulation of its target proteins.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Apr 17;4(4):601-12. doi: 10.1021/cn300218d. Epub 2013 Feb 5. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23384199 Free PMC article.
-
Sorcin links calcium signaling to vesicle trafficking, regulates Polo-like kinase 1 and is necessary for mitosis.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 10;9(1):e85438. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085438. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24427308 Free PMC article.
-
The solution structure of a plant calmodulin and the CaM-binding domain of the vacuolar calcium-ATPase BCA1 reveals a new binding and activation mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 3;285(49):38502-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.131201. Epub 2010 Sep 29. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20880850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berggård T., Arrigoni G, Olsson O., Fex M., Linse S., James P. (2006) 140 mouse brain proteins identified by Ca2+-calmodulin affinity chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res 5, 669–687 - PubMed
-
- Larkin D., Murphy D., Reilly D. F., Cahill M., Sattler E., Harriott P., Cahill D. J., Moran N. (2004) ICln, a novel integrin alpha IIb beta 3 associated protein, functionally regulates platelet activation. J. Biol. Chem 279, 27286–27293 - PubMed
-
- Xia Z., Storm D. R. (2005) The role of calmodulin as a signal integrator for synaptic plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci 6, 267–276 - PubMed
-
- Kahl C. R., Means A. R. (2003) Regulation of cell cycle progression by calcium/calmodulin-dependent pathways. Endocr. Rev 24, 719–736 - PubMed
-
- Clapham D. E. (2007) Calcium signaling. Cell 131, 1047–1058 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

