Molecular construction and optimization of anti-human IL-1alpha/beta dual variable domain immunoglobulin (DVD-Ig) molecules
- PMID: 20068402
- PMCID: PMC2726605
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.1.4.8755
Molecular construction and optimization of anti-human IL-1alpha/beta dual variable domain immunoglobulin (DVD-Ig) molecules
Abstract
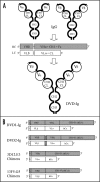
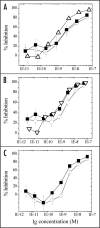
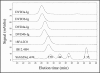
Signal transduction through the interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) pathway mediates a strong pro-inflammatory response, which contributes to a number of human diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Within the IL-1 family, IL-1alpha and IL-1beta are both agonistic ligands for IL-1R, whereas IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) is an endogenous antagonist that binds to IL-R, but does not signal. Therefore, the ideal therapeutic strategy would be blocking both IL-1alpha and IL-1beta, but not IL-1ra. However, due to low sequence homology between the three members of the family, it has been exceedingly difficult to identify potent therapeutic agents, e.g., monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), that selectively recognize both IL-1alpha and IL-1beta, but not IL-1ra. Currently, several anti-IL-1 therapeutic agents in clinical development either inhibit only IL-1beta (i.e., anti-IL-1beta mAb), or recognize all three ligands (i.e., anti-IL-1R mAb or IL-1R Trap). We have recently developed a novel dual variable domain immunoglobulin (or DVD-Ig) technology that enables engineering the distinct specificities of two mAbs into a single functional, dual-specific, tetravalent IgG-like molecule. Based on this approach, we have developed anti-human IL-1alpha/beta DVD-Ig molecules using several pairs of monoclonal antibodies with therapeutic potential, and present a case study for optimal design of a DVD-Ig agent for a specific target pair combination.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Generation and characterization of ABT-981, a dual variable domain immunoglobulin (DVD-Ig(TM)) molecule that specifically and potently neutralizes both IL-1α and IL-1β.MAbs. 2015;7(3):605-19. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1026501. MAbs. 2015. PMID: 25764208 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and Tolerability of a Dual Variable Domain Immunoglobulin ABT-981 Against IL-1α and IL-1β in Healthy Subjects and Patients With Osteoarthritis of the Knee.J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;56(12):1582-1590. doi: 10.1002/jcph.764. Epub 2016 Jun 2. J Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27150261 Clinical Trial.
-
Generation of dual-variable-domain immunoglobulin molecules for dual-specific targeting.Methods Enzymol. 2012;502:25-41. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416039-2.00002-1. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22208980
-
Anti-IL-1 molecules: new comers and new indications.Joint Bone Spine. 2010 Mar;77(2):102-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2009.10.011. Epub 2009 Dec 31. Joint Bone Spine. 2010. PMID: 20045371 Review.
-
Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment by Intervention in Interleukin-1 Biology.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(32):4893-4905. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170613080919. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28606052 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a bispecific CDH17-GUCY2C ADC bearing the ferroptosis inducer RSL3 for the treatment of colorectal cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jul 28;11(1):347. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02652-0. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40721409 Free PMC article.
-
A series of anti-CEA/anti-DOTA bispecific antibody formats evaluated for pre-targeting: comparison of tumor uptake and blood clearance.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2013 Mar;26(3):187-93. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzs096. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2013. PMID: 23175797 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Antibody Design.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2015;17:191-216. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071114-040733. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2015. PMID: 26274600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies and challenges for the next generation of therapeutic antibodies.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 May;10(5):345-52. doi: 10.1038/nri2747. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20414207 Review.
-
Grabbing the Bull by Both Horns: Bovine Ultralong CDR-H3 Paratopes Enable Engineering of 'Almost Natural' Common Light Chain Bispecific Antibodies Suitable For Effector Cell Redirection.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 11;12:801368. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.801368. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35087526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apte RN, Voronov E. Is interleukin-1 a good or bad ‘guy’ in tumor immunobiology and immunotherapy? Immunol Rev. 2008;222:222–241. - PubMed
-
- Wu C, Ying H, Grinnell C, Bryant S, Miller R, Clabbers A, et al. Simultaneous targeting of multiple disease mediators by a dual-variable-domain immunoglobulin. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1290–1297. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
