The interaction between tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis and its receptor fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 promotes the recruitment of neutrophils into the ischemic brain
- PMID: 20068578
- PMCID: PMC2949208
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.280
The interaction between tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis and its receptor fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 promotes the recruitment of neutrophils into the ischemic brain
Abstract
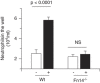
Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and its receptor fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (Fn14) are expressed in endothelial cells and perivascular astrocytes. Here, we show that TWEAK induces a dose-dependent increase in the expression of the chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in astrocytes, and that this effect is mediated by its interaction with Fn14 via nuclear factor-kappaB pathway activation. Exposure to oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) conditions increases TWEAK and Fn14 mRNA expression in wild-type (Wt) astrocytic cultures. Likewise, incubation under OGD conditions induces the expression of MCP-1 in Wt astrocytes but not in astrocytes deficient on either TWEAK (TWEAK(-/-)) or Fn14 (Fn14(-/-)). We also found that TWEAK induces the passage of neutrophils to the abluminal side of an in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier. Our earlier studies indicate that cerebral ischemia increases the expression of TWEAK and Fn14 in the endothelial cell-basement membrane-astrocyte interface. Here, we report that middle cerebral artery occlusion increases the expression of MCP-1 and the recruitment of neutrophils into the ischemic tissue in Wt but not in TWEAK(-/-) or Fn14(-/-) mice. These novel results indicate that during cerebral ischemia, the interaction between TWEAK and Fn14 leads to the recruitment of leukocytes into the ischemic tissue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis and fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 mediate cerebral ischemia-induced poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation and neuronal death.Neuroscience. 2010 Dec 29;171(4):1256-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.10.029. Epub 2010 Oct 16. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20955770 Free PMC article.
-
The cytokine tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis and its receptor fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 have a neuroprotective effect in the central nervous system.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Mar 6;9:45. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-45. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22394384 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis or Fn14 deficiency reduce elastase perfusion-induced aortic abdominal aneurysm in mice.J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 Aug 4;3(4):e000723. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000723. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014. PMID: 25092786 Free PMC article.
-
TWEAK/Fn14 pathway: an immunological switch for shaping tissue responses.Immunol Rev. 2011 Nov;244(1):99-114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01054.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22017434 Review.
-
The TWEAK-Fn14 system as a potential drug target.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;170(4):748-64. doi: 10.1111/bph.12337. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23957828 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Neuroinflammation: What Role for the Tumor Necrosis Factor-Like Weak Inducer of Apoptosis/Fn14 Pathway?Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 16;8:1534. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01534. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29201025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCL2 (C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2) Biomarker Responses in Central Versus Peripheral Compartments After Focal Cerebral Ischemia.Stroke. 2021 Nov;52(11):3670-3679. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032782. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Stroke. 2021. PMID: 34587791 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis and fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 mediate cerebral ischemia-induced poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation and neuronal death.Neuroscience. 2010 Dec 29;171(4):1256-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.10.029. Epub 2010 Oct 16. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20955770 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis promotes blood brain barrier disruption and increases neuronal cell death in MRL/lpr mice.J Autoimmun. 2015 Jun;60:40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Autoimmun. 2015. PMID: 25911200 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Like Weak Inducer of Apoptosis (TWEAK)/Fibroblast Growth Factor-Inducible 14 (Fn14) Axis in Cardiovascular Diseases: Progress and Challenges.Cells. 2020 Feb 11;9(2):405. doi: 10.3390/cells9020405. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32053869 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bossen C, Ingold K, Tardivel A, Bodmer JL, Gaide O, Hertig S, Ambrose C, Tschopp J, Schneider P. Interactions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and TNF receptor family members in the mouse and human. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:13964–13971. - PubMed
-
- Bover LC, Cardo-Vila M, Kuniyasu A, Sun J, Rangel R, Takeya M, Aggarwal BB, Arap W, Pasqualini R. A previously unrecognized protein-protein interaction between TWEAK and CD163: potential biological implications. J Immunol. 2007;178:8183–8194. - PubMed
-
- Carlos TM, Harlan JM. Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion molecules. Blood. 1994;84:2068–2101. - PubMed
-
- Che X, Ye W, Panga L, Wu DC, Yang GY. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expressed in neurons and astrocytes during focal ischemia in mice. Brain Res. 2001;902:171–177. - PubMed
-
- Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H, Hsu YM, Scott H, Hession C, Garcia I, Browning JL. TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32401–32410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

