Quantitative functional magnetic resonance imaging of brain activity using bolus-tracking arterial spin labeling
- PMID: 20068581
- PMCID: PMC2949184
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.284
Quantitative functional magnetic resonance imaging of brain activity using bolus-tracking arterial spin labeling
Abstract
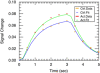
Blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is the most widely used method for mapping neural activity in the brain. The interpretation of altered BOLD signals is problematic when cerebral blood flow (CBF) or cerebral blood volume change because of aging and/or neurodegenerative diseases. In this study, a recently developed quantitative arterial spin labeling (ASL) approach, bolus-tracking ASL (btASL), was applied to an fMRI experiment in the rat brain. The mean transit time (MTT), capillary transit time (CTT), relative cerebral blood volume of labeled water (rCBV(lw)), relative cerebral blood flow (rCBF), and perfusion coefficient in the forelimb region of the somatosensory cortex were quantified during neuronal activation and in the resting state. The average MTT and CTT were 1.939+/-0.175 and 1.606+/-0.106 secs, respectively, in the resting state. Both times decreased significantly to 1.616+/-0.207 and 1.305+/-0.201 secs, respectively, during activation. The rCBV(lw), rCBF, and perfusion coefficient increased on average by a factor of 1.123+/-0.006, 1.353+/-0.078, and 1.479+/-0.148, respectively, during activation. In contrast to BOLD techniques, btASL yields physiologically relevant indices of the functional hyperemia that accompanies neuronal activation.
Figures




References
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA. Multisection cerebral blood flow MR imaging with continuous arterial spin labeling. Radiology. 1998;208:410–416. - PubMed
-
- Bandettini PA, Wong EC, Hinks SR, Tikofsky RS, Hyde JS. Time course EPI of human brain function during task activation. Magn Reson Med. 1992;25:390–397. - PubMed
-
- Belliveau JW, Kennedy DN, Jr, McKinstry RC, Buchbinder BR, Weisskoff RM, Cohen MS, Vevea JM, Brady TJ, Rosen BR. Functional mapping of the human visual cortex by magnetic resonance imaging. Science. 1991;254:716–719. - PubMed
-
- Bulte DP, Drescher K, Jezzard P. Comparison of hypercapnia-based calibration techniques for measurement of cerebral oxygen metabolism with MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2009;61:391–398. - PubMed
-
- Buxton RB, Frank LR. A model for the coupling between cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism during neural stimulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:64–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

