Preaxial polydactyly/triphalangeal thumb is associated with changed transcription factor-binding affinity in a family with a novel point mutation in the long-range cis-regulatory element ZRS
- PMID: 20068592
- PMCID: PMC2987342
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2009.225
Preaxial polydactyly/triphalangeal thumb is associated with changed transcription factor-binding affinity in a family with a novel point mutation in the long-range cis-regulatory element ZRS
Abstract
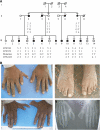
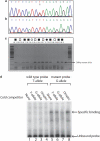
A cis-regulatory sequence also known as zone of polarizing activity (ZPA) regulatory sequence (ZRS) located in intron 5 of LMBR1 is essential for expression of sonic hedgehog (SHH) in the developing posterior limb bud mesenchyme. Even though many point mutations causing preaxial duplication defects have been reported in ZRS, the underlying regulatory mechanism is still unknown. In this study, we analyzed the effect on transcription factor binding of a novel ZRS point mutation (463T>G) in a Pakistani family with preaxial polydactyly and triphalangeal thumb. Electrophoretical mobility shift assay demonstrated a marked difference between wild-type and the mutant probe, which uniquely bound one or several transcription factors extracted from Caco-2 cells. This finding supports a model in which ectopic anterior SHH expression in the developing limb results from abnormal binding of one or more transcription factors to the mutant sequence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Two novel point mutations in the long-range SHH enhancer in three families with triphalangeal thumb and preaxial polydactyly.Am J Med Genet A. 2007 Jan 1;143A(1):27-32. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31563. Am J Med Genet A. 2007. PMID: 17152067
-
A novel ZRS variant causes preaxial polydactyly type I by increased sonic hedgehog expression in the developing limb bud.Genet Med. 2020 Jan;22(1):189-198. doi: 10.1038/s41436-019-0626-7. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Genet Med. 2020. PMID: 31395945 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mutation in the SHH long-range regulator (ZRS) is associated with preaxial polydactyly, triphalangeal thumb, and severe radial ray deficiency.Am J Med Genet A. 2012 Oct;158A(10):2610-5. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35584. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Am J Med Genet A. 2012. PMID: 22903933
-
Zone of Polarizing Activity Regulatory Sequence Mutations/Duplications with Preaxial Polydactyly and Longitudinal Preaxial Ray Deficiency in the Phenotype: A Review of Human Cases, Animal Models, and Insights Regarding the Pathogenesis.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Feb 13;2018:1573871. doi: 10.1155/2018/1573871. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29651423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tibial hemimelia-polydactyly-five-fingered hand syndrome associated with a 404 G>A mutation in a distant sonic hedgehog cis-regulator (ZRS): a case report.J Pediatr Orthop B. 2013 May;22(3):219-21. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0b013e32835106b2. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2013. PMID: 22314436 Review.
Cited by
-
The disruption of a novel limb cis-regulatory element of SHH is associated with autosomal dominant preaxial polydactyly-hypertrichosis.Eur J Hum Genet. 2016 Jan;24(1):37-43. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2015.53. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 25782671 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive In Vivo Interrogation Reveals Phenotypic Impact of Human Enhancer Variants.Cell. 2020 Mar 19;180(6):1262-1271.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.031. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32169219 Free PMC article.
-
A novel ZRS mutation leads to preaxial polydactyly type 2 in a heterozygous form and Werner mesomelic syndrome in a homozygous form.Hum Mutat. 2014 Aug;35(8):945-8. doi: 10.1002/humu.22581. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Hum Mutat. 2014. PMID: 24777739 Free PMC article.
-
The Story of the Hand.Indian J Plast Surg. 2021 Apr;54(2):106-113. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1729771. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Indian J Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 34239230 Free PMC article.
-
A novel 13 base pair insertion in the sonic hedgehog ZRS limb enhancer (ZRS/LMBR1) causes preaxial polydactyly with triphalangeal thumb.Hum Mutat. 2012 Jul;33(7):1063-6. doi: 10.1002/humu.22097. Epub 2012 May 11. Hum Mutat. 2012. PMID: 22495965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lettice LA, Heaney SJ, Purdie LA, et al. A long-range Shh enhancer regulates expression in the developing limb and fin and is associated with preaxial polydactyly. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:1725–1735. - PubMed
-
- Sagai T, Masuya H, Tamura M, et al. Phylogenetic conservation of a limb-specific, cis-acting regulator of sonic hedgehog (Shh) Mamm Genome. 2004;15:23–34. - PubMed
-
- Klopocki E, Ott CE, Benatar N, Ullmann R, Mundlos S, Lehmann K. A microduplication of the long range SHH limb regulator (ZRS) is associated with triphalangeal thumb-polysyndactyly syndrome. J Med Genet. 2008;45:370–375. - PubMed
-
- Sun M, Ma F, Zeng X, et al. Triphalangeal thumb-polysyndactyly syndrome and syndactyly type IV are caused by genomic duplications involving the long range, limb-specific SHH enhancer. J Med Genet. 2008;45:589–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

